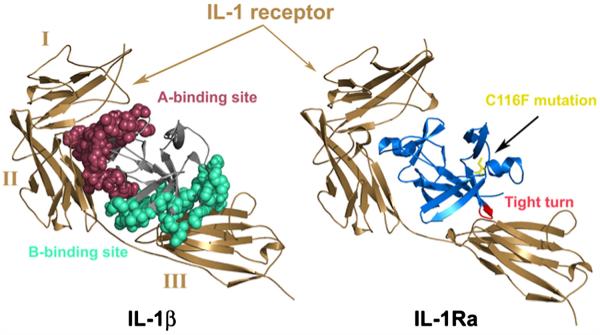
Fig. 1.
(a) Comparison of IL-1β (left) and IL-1Ra (right) bound to the IL-1RI receptor. Ig domains I, II, and III of sIL-1RI are labeled on the complex on the left for clarity. IL-1β is thought to induce a conformational change (helical structure in the linker between domains II and III and a 20° rotation of Ig domain III with respect to that observed in the IL-1RI complex of IL-1Ra) and binds the third domain of the receptor. The binding sites in IL-1β are highlighted in red (binding site A) and cyan (binding site B), respectively. When bound to IL-1β, contacts in binding site B result in a closed conformation of the receptor domains while the receptor adopts an inactive open conformation when bound to IL-1Ra. (b) The heterotrimeric complex of IL-1RI (brown) and co-receptor, IL-1RAcP (magenta), modeled with IL-1Ra (blue). The C116F mutation (yellow) is highlighted to illustrate the location of the change with respect to the receptor as well as the barrel core of the protein.