Figure 2. β-lactam-induced ROS production is associated with DNA damage and activation of the SOS response.
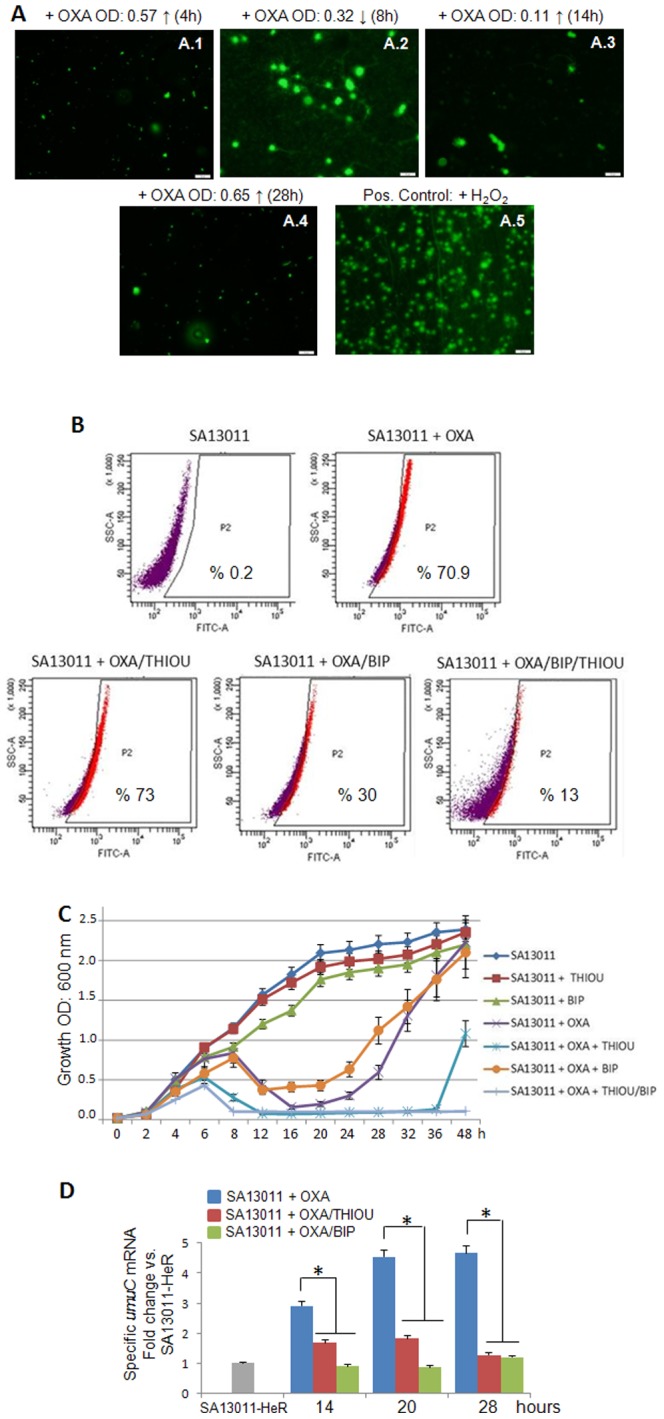
A) DNA fragmentation was analyzed by CometAssay™. SA13011-HeR + OXA (0.5 µg/ml) was collected and processed as described in Methods; nucleoids showing either no signs (A1; OD600 nm: 0.57, 4 h) or fragmented DNA (spread, larger and more diffuse; A2-A3, OD600 nm: 0.32, 8 h; 0.11, 14 h; respectively) are shown. A.4: nucleoids corresponding to OD600 nm: 0.65, 28 h, without significant DNA fragmentation. A.5: SA13011-HeR cells were exposed overnight to 1 mM H2O2 and used as a positive control for DNA damage/fragmentation. B) ROS production following exposure to β-lactam ± thiourea (THIOU; radical scavenger) and/or 2,2′-bipyridyl (BIP; interferes with the Fenton reaction) was measured by flow cytometry using the reporter dye HPF in SA13011-HeR ± OXA (0.5 µg/ml) ± ThioU (120 mM), and ± BIP (0.25 mM), collected after 16 hours of exposure to these conditions; results are representative of one experiment performed in triplicate; additional experiments gave similar results. C) Time-course analysis of SA13011 HeR-HoR (OD600) in cells grown ± OXA (0.5 µg/ml), ± thiourea (120 mM, THIOU) or bipyridyl (0.25 mM, BIP). D) Quantitation of umuC mRNA expression levels (involved in activation of SOS response) by real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR using samples grown as indicated in C. Relative fold-change values (SA13011-HeR reference value = 1) of specific mRNAs are shown on the vertical axis. 16S rRNA was used as an internal control. *, P<0.01, statistically significant vs. corresponding reference value.
