Figure 6.
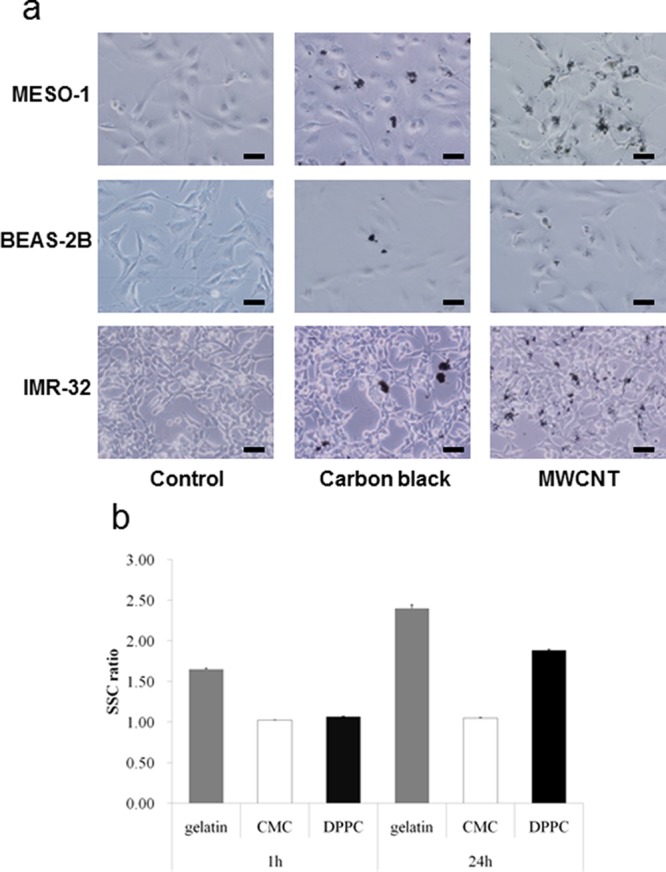
Cellular uptake of pristine MWCNTs varies depending on the type of cell and the choice of dispersant. (a) Combined images from bright field images and phase-contrast photomicrographs obtained 24 h after exposure of human malignant pleural mesothelioma cells (MESO-1), human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B), and human neuroblasts (IMR-32) to carbon black (CB, 50 nm diameter) and MWCNTs. Both CB and MWCNTs were absorbed in the MESO-1 cells and BEAS-2B cells, and localized around the respective exposure sites, whereas in the case of the IMR-32 cells, both CB and MWCNTs adhered but failed to be absorbed. CB and MWCNTs were added at 1 μg/mL for the treatment of BEAS-2B cells, and 10 μg/mL for the treatment of the other cells. Scale bars = 50 μm. Reprinted with permission from ref (384). Copyright 2011 Nature Publishing Group. (b) A comparison of cellular uptake in BEAS-2B observed 1 and 24 h after exposure to MWCNTs dispersed using different dispersants. Cellular uptake was determined in terms of the intensity of side scattered light (SSC) from MWCNTs absorbed in the cells using a flow cytometer. The MWCNTs dispersed in gelatin or 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) were increasingly absorbed over time, whereas those dispersed in carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) were little absorbed in the cells. Reprinted with permission from ref (385). Copyright 2011 Dove Medical Press.
