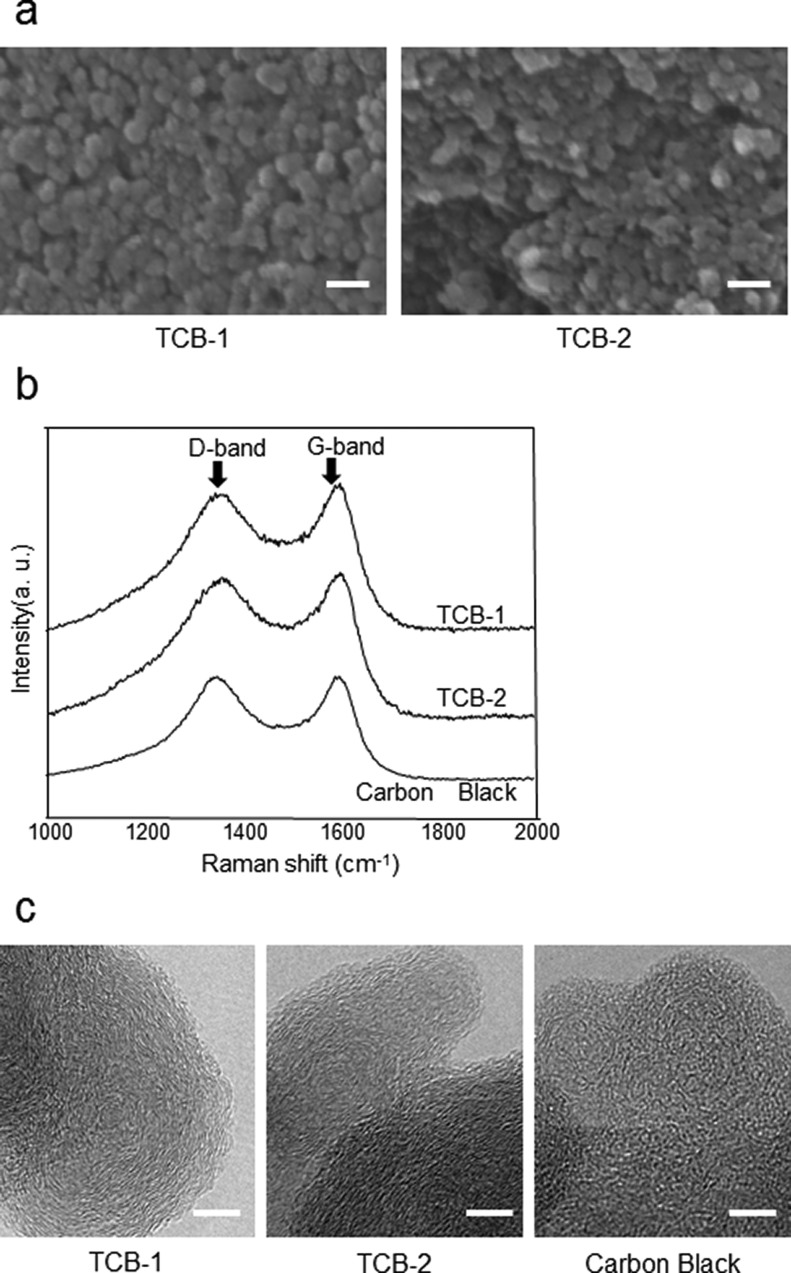
Figure 8.
Having historically been proven safe to the human body, tattoos comprise nanosized highly pure carbon black, and hence serve well as a reference material for evaluating the safety of CNTs, which likewise occur in the form of nanosized carbon particles. (a) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of tattoo carbon black-1 (TCB-1) and tattoo carbon black-2 (TCB-2) prepared by drying two different tattoos. TCB-1 and TCB-2 were found to have accumulated in the form of generally regular particles having a diameter of about 30–50 nm, and generally irregular particles having a diameter of about 50 nm, respectively. (b) Raman analysis of TCB-1, TCB-2, and ordinary carbon black. TCB-1 and TCB-2 exhibited nearly the same Raman shift pattern as with ordinary carbon black. D-band, turbostratic amorphous; G band, graphite crystal. (c) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of TCB-1, TCB-2, and ordinary carbon black. These three substances were found to have nearly the same particle shape. Reprinted with permission from ref (97). Copyright 2011 Elsevier.