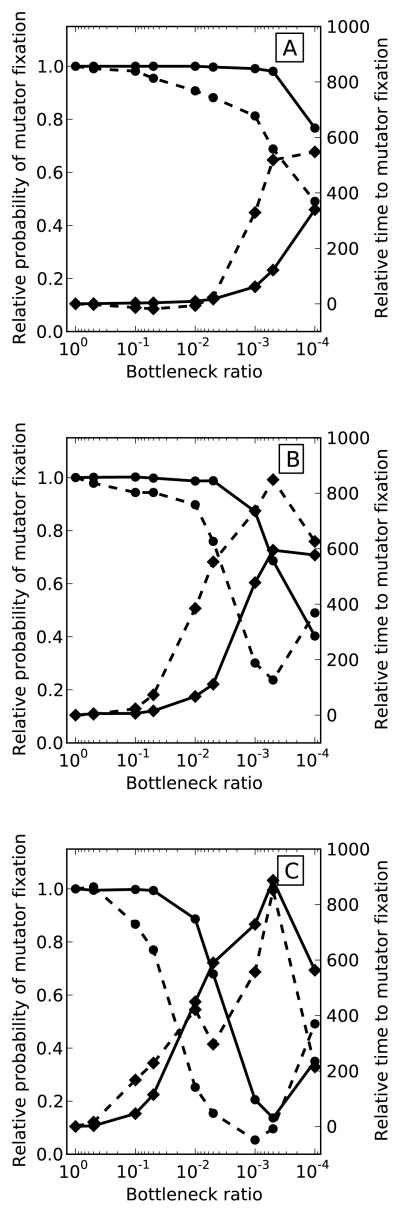
Figure 1. The effect of population bottlenecks on mutator dynamics at different supply rates of beneficial mutations in simulated populations.
Probability of mutator fixation (solid lines) generally declined with smaller bottlenecks while the time to mutator fixation (dashed lines) increased and became more variable. Bottlenecks were particularly effective at smaller beneficial mutation supply rates. The supply rate of beneficial mutations, NUb, was adjusted by varying the population size, N, between 105 (Column 1), 106 (Column 2), and 107 (Column 3) individuals and beneficial mutation rate, Ub, between 10−6 (Row 1), 10−7 (Row 2), and 10−8 (Row3) mutations per individual per generation. Beneficial mutations were drawn from a exponential distribution with mean 0.05 and the mutator increased the mutation rate 50-fold. Error bars on the time to fixation represent 1 standard deviation. Results are averaged over 1000 runs of the simulation.