TABLE IV.
Prevention and treatment of common complications of dexamethasone therapy
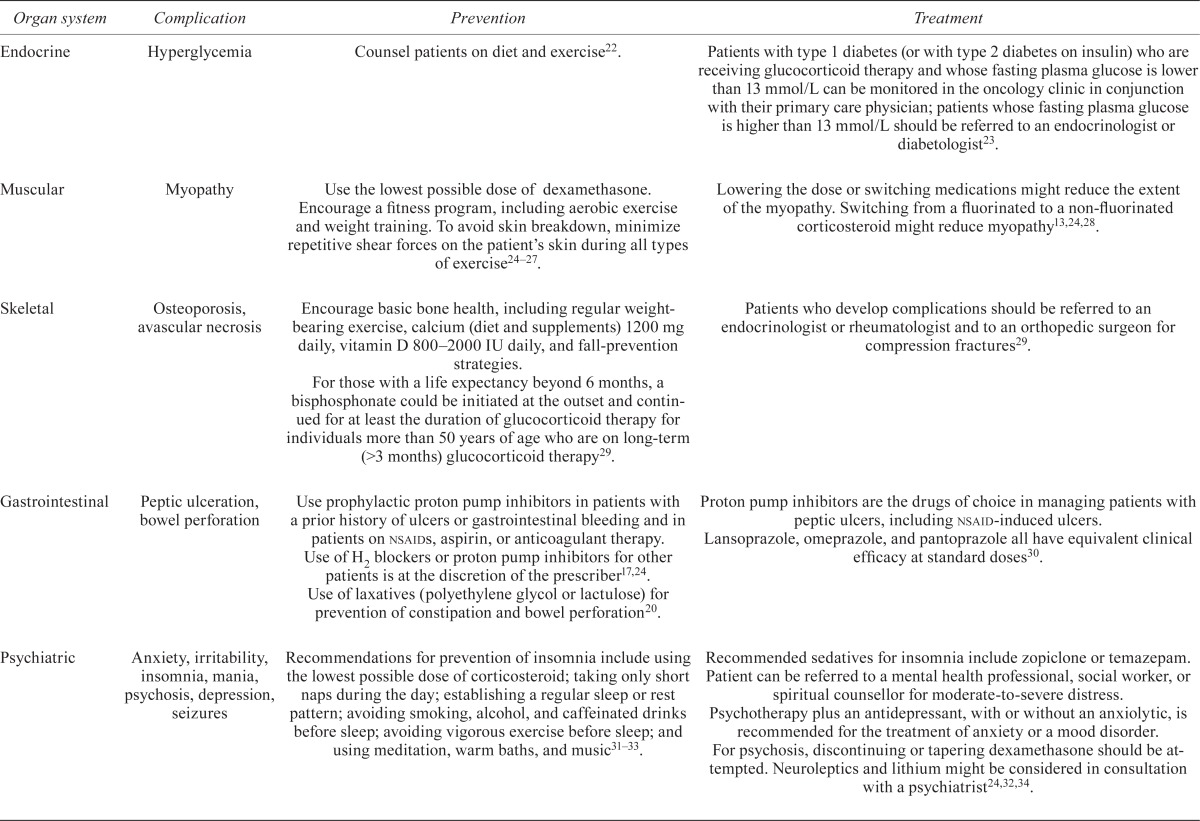
| Organ system | Complication | Prevention | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endocrine | Hyperglycemia | Counsel patients on diet and exercise22. | Patients with type 1 diabetes (or with type 2 diabetes on insulin) who are receiving glucocorticoid therapy and whose fasting plasma glucose is lower than 13 mmol/L can be monitored in the oncology clinic in conjunction with their primary care physician; patients whose fasting plasma glucose is higher than 13 mmol/L should be referred to an endocrinologist or diabetologist23. |
| Muscular | Myopathy | Use the lowest possible dose of dexamethasone. Encourage a fitness program, including aerobic exercise and weight training. To avoid skin breakdown, minimize repetitive shear forces on the patient’s skin during all types of exercise24–27. | Lowering the dose or switching medications might reduce the extent of the myopathy. Switching from a fluorinated to a non-fluorinated corticosteroid might reduce myopathy13,24,28. |
| Skeletal | Osteoporosis, avascular necrosis | Encourage basic bone health, including regular weight-bearing exercise, calcium (diet and supplements) 1200 mg daily, vitamin D 800–2000 IU daily, and fall-prevention strategies. For those with a life expectancy beyond 6 months, a bisphosphonate could be initiated at the outset and continued for at least the duration of glucocorticoid therapy for individuals more than 50 years of age who are on long-term (>3 months) glucocorticoid therapy29. |
Patients who develop complications should be referred to an endocrinologist or rheumatologist and to an orthopedic surgeon for compression fractures29. |
| Gastrointestinal | Peptic ulceration, bowel perforation | Use prophylactic proton pump inhibitors in patients with a prior history of ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding and in patients on nsaids, aspirin, or anticoagulant therapy. Use of H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors for other patients is at the discretion of the prescriber17,24. Use of laxatives (polyethylene glycol or lactulose) for prevention of constipation and bowel perforation20. |
Proton pump inhibitors are the drugs of choice in managing patients with peptic ulcers, including nsaid-induced ulcers. Lansoprazole, omeprazole, and pantoprazole all have equivalent clinical efficacy at standard doses 30. |
| Psychiatric | Anxiety, irritability, insomnia, mania, psychosis, depression, seizures | Recommendations for prevention of insomnia include using the lowest possible dose of corticosteroid; taking only short naps during the day; establishing a regular sleep or rest pattern; avoiding smoking, alcohol, and caffeinated drinks before sleep; avoiding vigorous exercise before sleep; and using meditation, warm baths, and music31–33. | Recommended sedatives for insomnia include zopiclone or temazepam. Patient can be referred to a mental health professional, social worker, or spiritual counsellor for moderate-to-severe distress. Psychotherapy plus an antidepressant, with or without an anxiolytic, is recommended for the treatment of anxiety or a mood disorder. For psychosis, discontinuing or tapering dexamethasone should be attempted. Neuroleptics and lithium might be considered in consultation with a psychiatrist24,32,34. |
| Infections | Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (pjp), candidiasis | Consider prophylactic therapy with trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole against pjp in brain cancer patients receiving prolonged corticosteroid therapy24,35. | Treatment of pjp infections with trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim plus dapsone, atovaquone suspension, clindamycin plus primaquine, or pentamidine. Treat oropharyngeal candidiasis with nystatin, fluconazole, or itraconazole 24,35. |
| Hematologic | Venous thromboembolism (vte) | Routine prophylaxis with an antithrombotic agent is not recommended. Prophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin (dalteparin, enoxaparin, tinzaparin), fondaparinux, unfractionated heparin, or warfarin might be warranted in individuals considered to be at risk of vte based on assessment of risk factors36,37. | Low molecular weight heparin is the preferred approach for cancer patients with established vte and for long-term anticoagulant therapy36,38. |
| Cardiovascular | Hypertension, cardiovascular risk | There is no clear evidence with respect to the prevention and treatment of corticosteroid-induced hypertension. Screening is recommended, particularly during the first months of therapy and in patients with corticosteroid-induced lipodystrophy26. |
nsaid = nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
