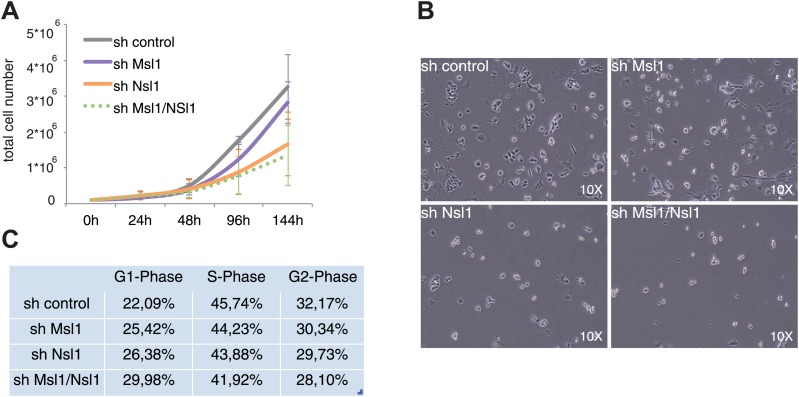
Figure 6. NSL influences cell growth and cell cycle of mESCs.
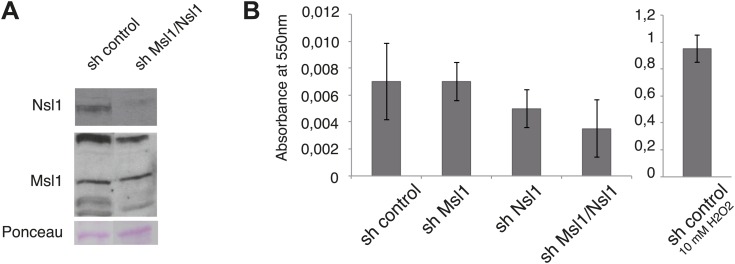
(A) Cell proliferation analyses by cell counting over 6 days of control, or indicated KD mESCs. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1A for validation of KD efficiency of sh Msl1/Nsl1 double KD mESCs. (B) Morphology of control and Msl1 and Nsl1 single or double KD mESCs at 6 days after lentiviral infection using a reverse-phase microscope with a 10x magnification. (C) Cell cycle analyses of control and KD mESCs by propidium iodide staining followed by FACS analyses. Cell numbers of G1-, S- or G2-phases are represented in percentages after analyses with CellQuest Pro software. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1B for apoptosis analysis.