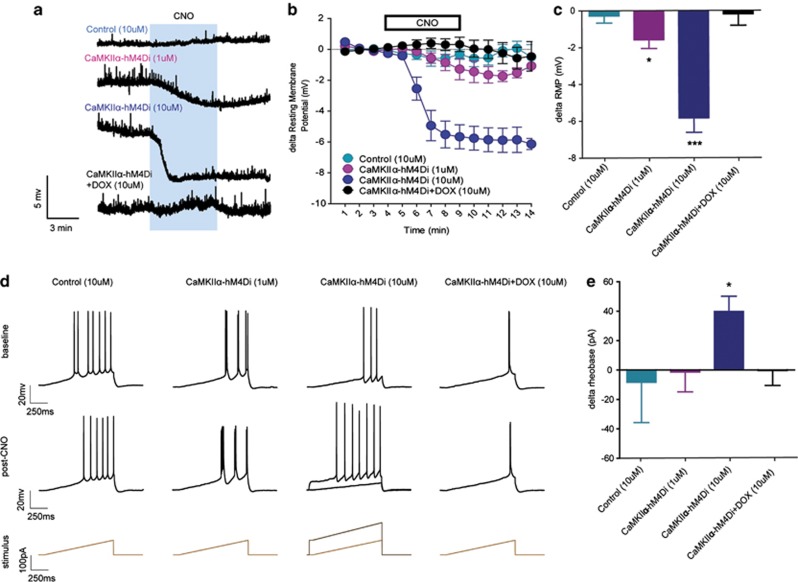
Figure 2.
Clozapine-n-oxide (CNO) dose-dependently decreased CA1 neuronal intrinsic excitability in CaMKIIα-hM4Di double transgenic mice. (a) Representative traces of resting membrane potential (RMP) from current-clamp electrophysiological recordings of CA1 pyramidal neurons in CaMKIIα- hM4Di double transgenic and control mice. (b, c). Five minutes bath application of 10 μM CNO hyperpolarized CA1 pyramidal neurons in double transgenic mice (p<0.001, n=6), which was greater than the 1 μM dose (p=0.004, n=4), but 10 μM CNO did not affect RMP in control mice or double transgenic mice pretreated with DOX (p's<0.45, n's=5 and 6, respectively). (d) Representative traces of current-injected firing in CA1 pyramidal neurons of CaMKIIα- hM4Di and control animals before (top) and after (middle) CNO administration, and stimulus waveform of current injection ramp used to determine the minimum current injection required to fire an action potential (rheobase; bottom). (e) The mean change from baseline in the rheobase after CNO administration, showing that bath application of 10 μM, but not 1 μM, CNO decreased the rheobase of CA1 neurons in double transgenic mice (10 μM: p=0.018, n=5, 1 μM: p<0.90, n=4) but not in controls or double transgenic mice pretreated with DOX (p's<0.75, n's=5 and 5, respectively).