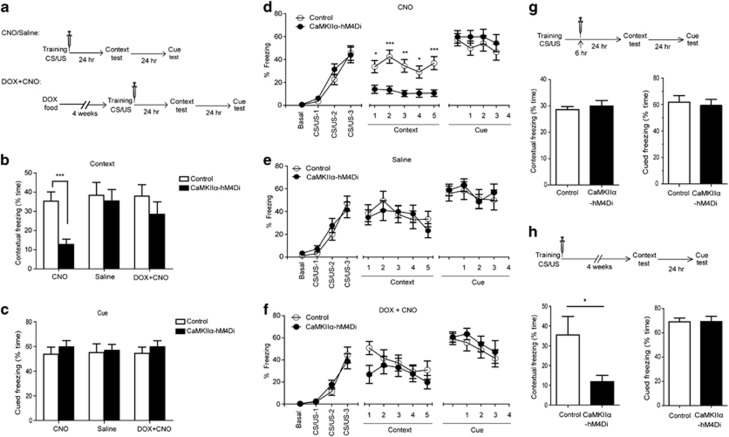
Figure 4.
Consolidation of contextual memory was disrupted in CaMKIIα-hM4Di mice when clozapine-n-oxide (CNO) was administrated immediately after training. (a) Experimental time-line for the fear-conditioning paradigm (b–f). Three doses of CNO (2 mg/kg) or saline were administrated at 0, 2, and 4 h after training. (b) Double transgenic mice showed a significant decrease in contextual freezing in CNO group (p=0.0003, DTg, n=16, control, n=17) but not in saline group (p=0.744, n=15) or DOX+CNO group (p=0.294, n=12). (c) There was no significant difference in cued freezing between two genotypes in all groups. (d–f) There was a comparable performance during training between two genotypes in all three groups. Contextual memory was shown as the percentage of freezing time in a 1-min block during 5-min test. Only the CNO groups showed a significant difference between double transgenic and control mice (p=0.0003). The cued memory was shown as the percentage of freezing time during the tone (CS). There was no significant difference between two genotypes in all groups. (g) Contextual memory was not impaired in double transgenic mice when CNO (2 mg/kg) was given 6, 8, and 10 h after training. Double transgenic mice showed no significant difference in contextual memory (p=0.555 DTg, n=9, control, n=11). (h) Remote contextual memory was impaired in double transgenic mice when CNO (2 mg/kg) was given at 0, 2, and 4 h after training, and contextual learning tested 1 month later. CaMKIIα-hM4Di mice exhibited a significant decrease in contextual memory (p=0.045, DTg, n=8, control, n=9).