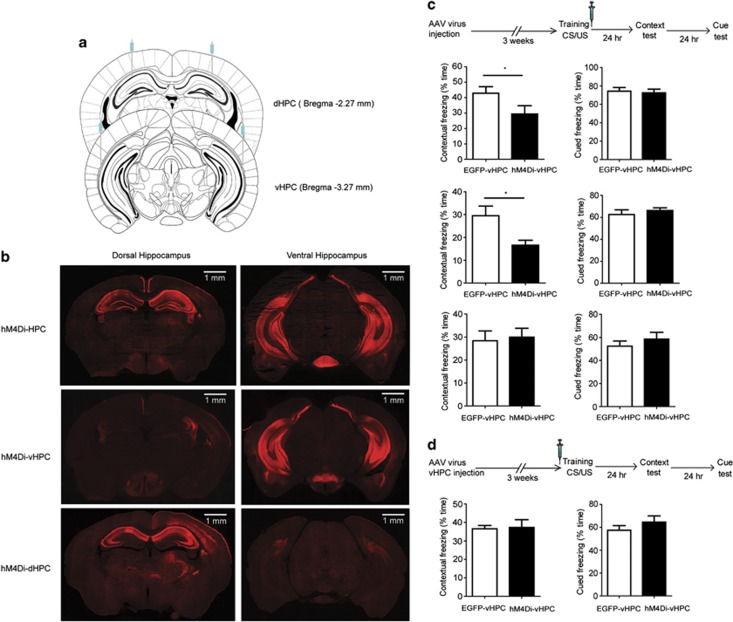
Figure 5.
Ventral, but not dorsal, hippocampus was involved in synaptic consolidation of contextual memory. (a) Schematic representation of viral delivery to the dorsal hippocampus (dHPC), ventral hippocampus (vHPC), or both (HPC). CaMKIIα::HA-hM4Di-IRES-mCitrine or CaMKIIα::EGFP viral vectors were bilaterally injected into dHPC, vHPC, or both. (b) Immunostaining of mouse brain delivered with CaMKIIα::HA-hM4Di-IRES-mCitrine virus. HA-hM4Di was expressed in the dorsal hippocampus, ventral hippocampus, or both in hM4Di-dHPC, hM4Di-vHPC, or hM4Di-HPC mice, respectively. Scale bar: 1 mm. (c) Ventral, but not dorsal, hippocampus was involved in synaptic consolidation of contextual memory. Three weeks after viral delivery, animals were trained and administrated with three doses of clozapine-n-oxide (CNO; 2 mg/kg) at 0, 2, and 4 h after training. Contextual and cued memories were tested 24 and 48 h later, respectively. Mice with HA-hM4Di viruses injected into both dHPC and vHPC showed a significant decrease in contextual memory compared with the control mice (p=0.047, n=8). Mice with HA-hM4Di viruses injected into only vHPC showed a significant decrease in contextual memory (p=0.015, n=10). However, mice with HA-hM4Di virus injected into only dHPC showed a similar freezing compared with the control mice in contextual memory (p=0.795, n=7). (d) Synaptic consolidation was not impaired by administration of CNO before training in hM4Di-vHPC mice. HA-hM4Di viruses were delivered to the vHPC. Three weeks later, mice were administrated with CNO (2 mg/kg) 30 min before, instead of after training. There was no significant difference in contextual memory between hM4Di-vHPC and control mice (p=0.87, n=9).