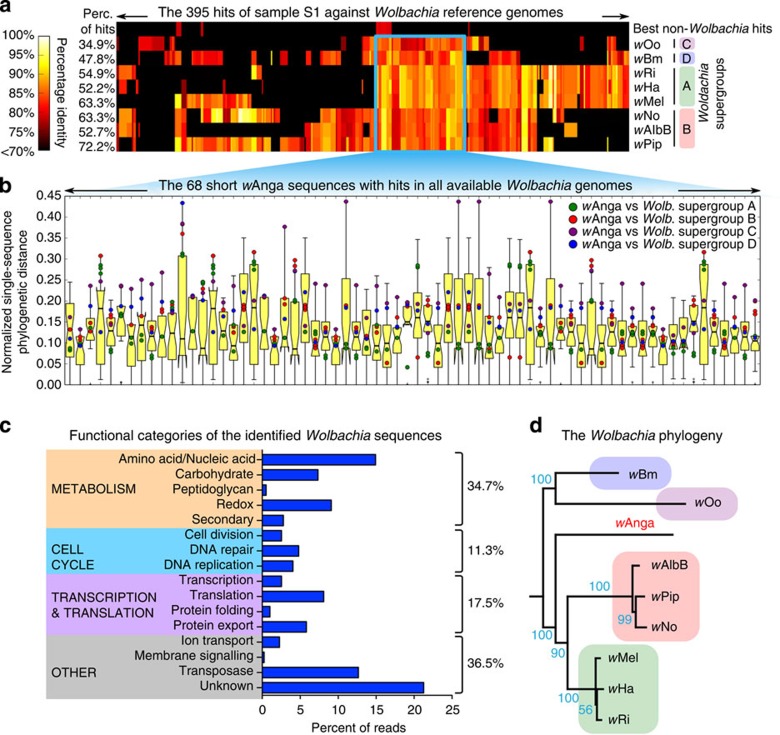
Figure 3. Whole-genome shotgun sequencing of a Wolbachia-positive sample identifies a new Wolbachia strain in An. gambiae.
Ovaries from a Wolbachia-positive female (sample S1) were sequenced using WGS. (a) Percentage (Perc.) identity of 395 short sequences uniquely attributable to Wolbachia from sample S1 versus eight sequenced strains. The Wolbachia reference strains and the supergroups are indicated with the corresponding percentage of assigned sequences. (b) Distribution of phylogenetic distances between different Wolbachia supergroups, from phylogenies reconstructed separately on each of the short sequences universally conserved within Wolbachia genomes (light blue inset in a). (c) Functional classification of Wolbachia loci identified by alignment to read sequences, based on NCBI annotated gene functions. (d) Wolbachia phylogeny, comprising the new Wolbachia strain wAnga isolated in An. gambiae, reconstructed from the concatenated sequences of b. These analyses show that wAnga is different from all other strains sequenced so far. The same analyses for another PCR-positive Wolbachia sample are available in Supplementary Fig. 3.