Fig. 2.
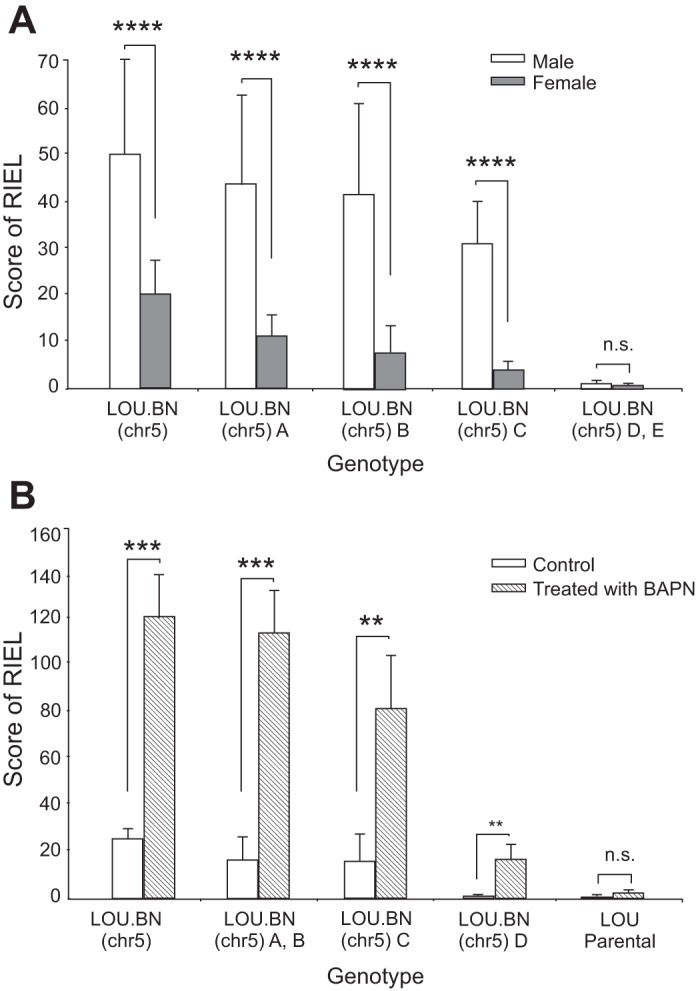
A: sex difference in congenic and subcongenic lines. A significant sex difference was observed for the RIEL score; n = 89, 36, 40, 66, 63 per genotype group for males, aged 20–40 wk, and 32, 28, 24, 29, 25 for females, aged 30–50 wk. Means ± SD. ****P <0.0001; n.s., nonsignificant. B: β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN)-treated congenic and subcongenic lines (aged 14–16 wk) exhibited significantly higher RIEL scores compared with untreated lines of similar genotype or with parental LOU rats. Interestingly, significant scores for RIEL were observed in the LOU.BN(chr5) D subcongenics after BAPN treatment; n = 8, 8, 4, 14, 6 per genotype group. Means ± SD; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.02.
