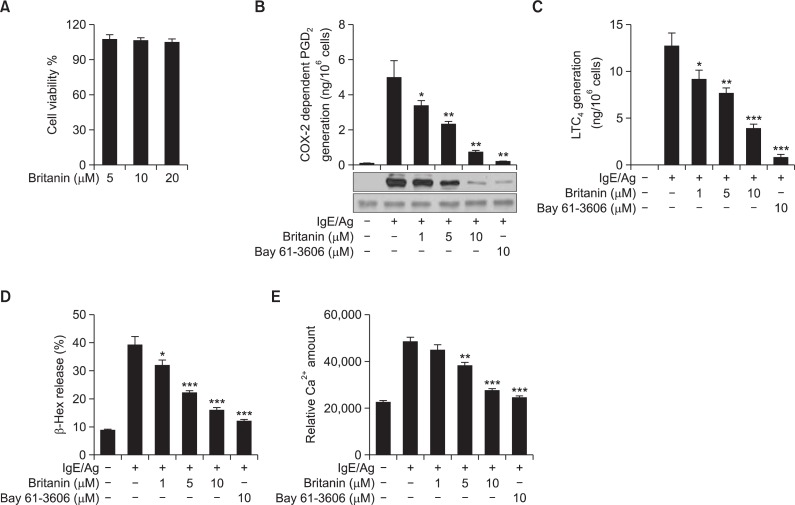
Fig. 1.
Effect of britanin on the cell viability, degranulation, PGD2 and LTC4 generation, and intracellular calcium increase in IgE/Ag-induced BMMCs. (A) BMMCs were incubated in the presence of 5, 10, or 20 μM of britanin. Cell viabilities were assayed using an MTT assay. Data represent means ± S.D of three different samples. (B) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were pre-incubated with 1 μg/ml aspirin for 2 h to abolish preexisting COX-1 activity, briefly washed, and then stimulated with DNP-HSA for 7 h. PGD2 released into the supernatant was quantified by a PGD2-MOX EIA kit and the cells were used for immunoblotting of COX-2 protein. (C) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were pre-incubated with the indicated concentrations of britanin or Bay 61-3606 for 1 h and stimulated with DNP-HSA for 15 min. LTC4 released into the supernatant was quantified using an enzyme immunoassay kit. (D) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were pre-incubated with the indicated concentrations of britanin or Bay 61-3606 for 1 h and stimulated with DNP-HSA for 15 min. β-Hex release in supernatants was measured as described in Materials and Methods. (E) IgE-sensitized BMMCs were pretreated with FluoForteTM Dye-Loading Solution for 1 h at room temperature. After washing the dye from cell surfaces with HBSS, cells were seeded into 96-well microplates, pre-incubated with britanin or Bay 61-3606 for 1 h, and stimulated with DNP-HSA. Relative calcium levels were measured using a flurometric imaging plated reader. Values are shown as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 versus the IgE/Ag-induced group.