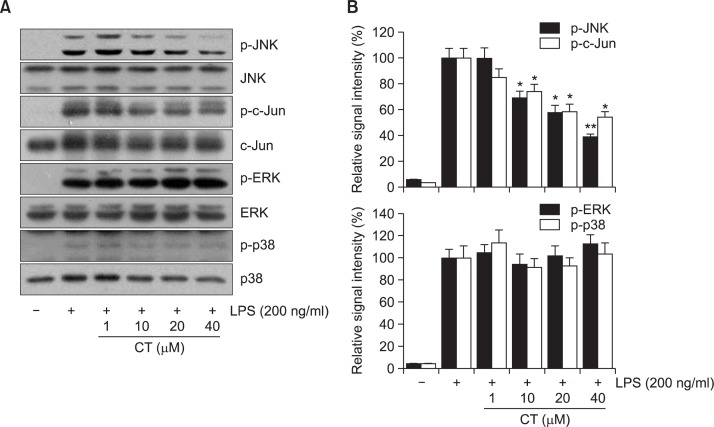
Fig. 5.
Effect of N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine on LPS-induced activation of MAPK signaling pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. (A) representative immunoblots, (B) quantitative analysis of immunoblots. Cellswere challenged with 200 ng/ml LPS in the absence or presence of N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine. LPS-induced increased phosphorylation of JNK and c-jun was significantly attenuated with N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine treatment. However, phosphorylation of ERK and p38 was not affected with N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine treatment, suggesting that JNK/c-jun signaling might play a key role in the LPS-induced activation of RAW264.7 cells. Images are representative of three independent experiments that shows reproducible results. The values are expressed as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 indicate statistically significant differences from treatments with LPS alone. CT stands for N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine.