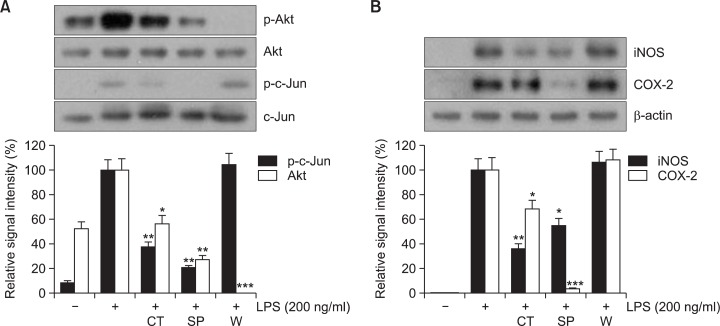
Fig. 7.
Role of JNK and Akt signaling pathways in N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine-mediated suppression of LPS-induced RAW264.7 cell activation. RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with CT (N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine), SP (SP600125, JNK inhibitor), or W (wortmannin, Akt inhibitor), and then exposed to LPS (200 ng/ml) for 1 hr. The cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blotting analysis. (A) Phosphorylation levels of Akt and c-jun were examined in the presence of CT, SP, or W. CT and SP significantly suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of Akt and c-jun. However, W did not inhibit LPS-induced c-jun phosphorylation. (B) The protein levels of iNOS and COX-2 were examined. Suppression of LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expressions were observed with N-(p-coumaryol) tryptamine (CT) and also with JNK inhibitor (SP) but not with Akt inhibitor (W). The images on top are representatives of three independent experiments. The data for quantitative analyses on bottom were obtained from three independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 indicate statistically significant differences from treatments with control alone.