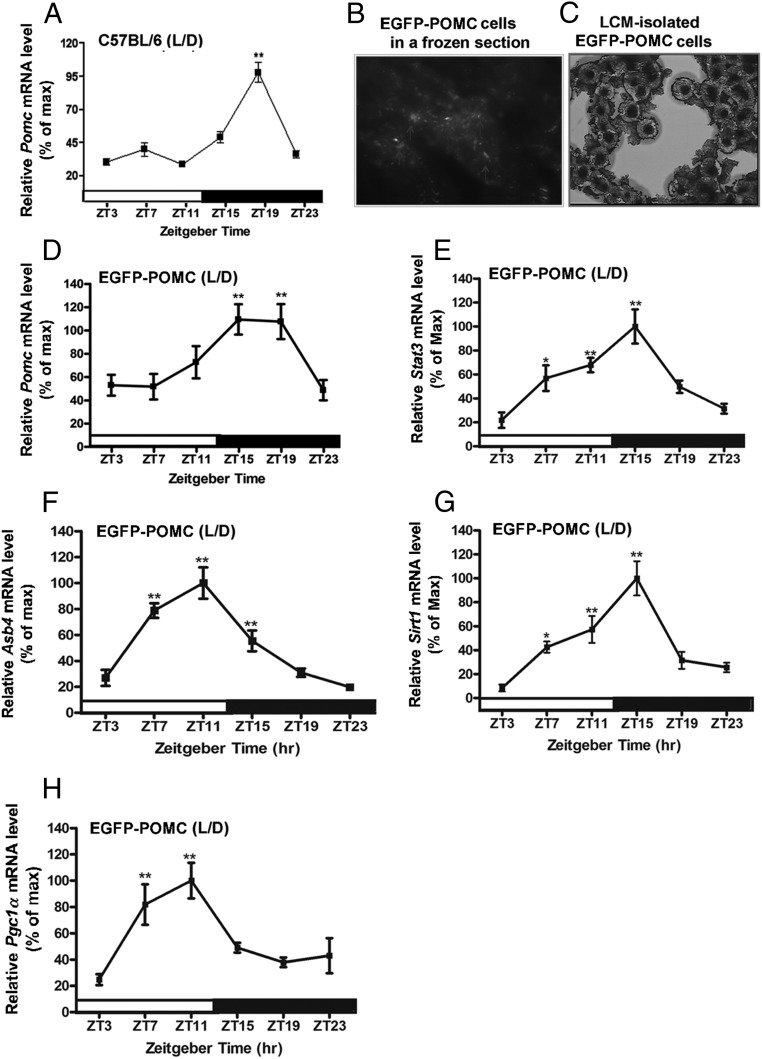
Figure 1.
Circadian expression of genes related to metabolic signaling in POMC neurons in the hypothalamus of wild-type and EGFP-POMC C57BL/6 mice under LD conditions. A, Daily rhythms in mRNA levels of the Pomc gene in the hypothalamic tissue of wild-type mice. B, Identification of POMC neurons (white arrowheads) by EGFP fluorescence. C, POMC neurons isolated in a LCM cap under a light microscope. D, Daily rhythms in mRNA levels of the Pomc gene in POMC neurons isolated by LCM from the hypothalamus of EGFP-POMC mice. E–H, Daily rhythms in the mRNA levels of metabolic-related genes (Stat3, E; Asb4, F; Sirt1, G; Pgc1a, H) in the POMC neurons of EGFP-POMC mice. The isolated Pomc cells correspond to brains collected at 10:00 am, 2:00 pm, 6:00 pm, 10:00 pm, 2:00 am, and 6:00 am. These time points correspond with ZT3, ZT7, ZT11, ZT15, ZT19, and ZT23, respectively. The mRNA level of Pomc or other metabolic gene at each time point was normalized with the Gapdh mRNA value, and the ratio was used to calculate the percentage of the maximum value over a 24-hour period. *, **, ***, Significantly different (P < .05, P < .01, P < .001, respectively) from the lowest value, as per a one-way ANOVA with the Dunnett posttest. Black bar represents the dark period. Data are mean ± SEM of five to six animals per time point.