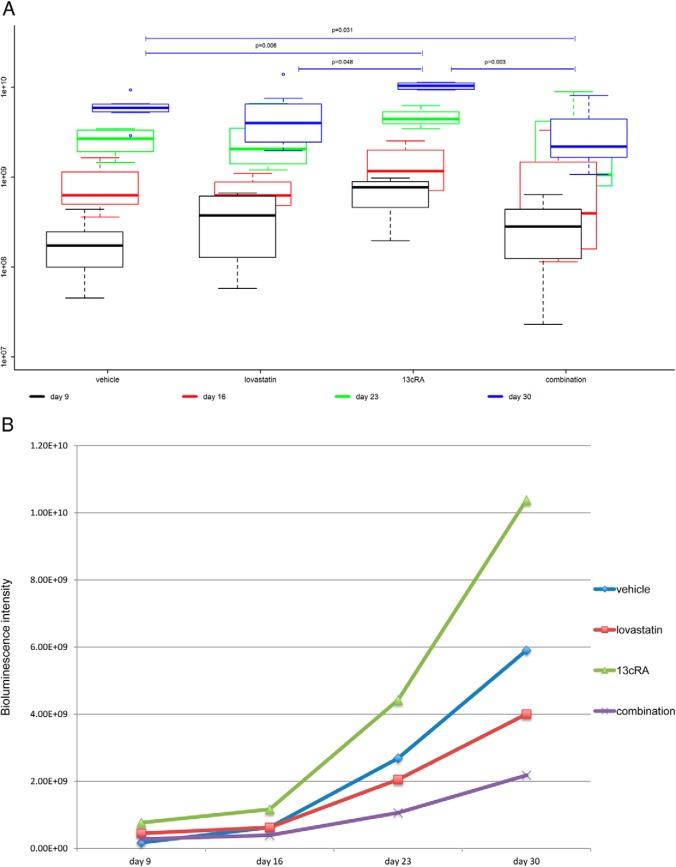
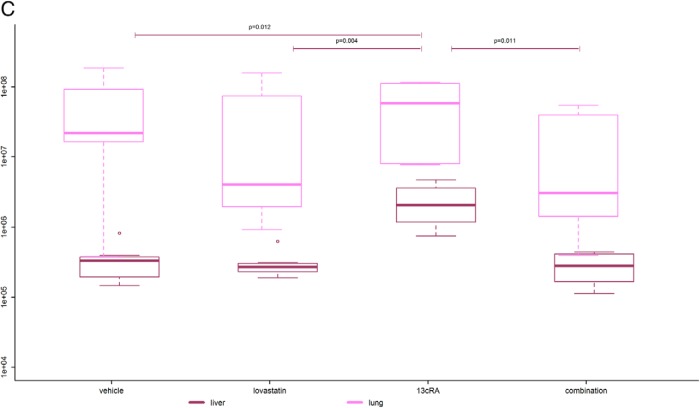
Figure 4.
Bioluminescence tumor imaging. A, Primary tumor luminescence. Boxplots are denoting median (thick line), quartiles (upper and lower margin of the box), maximum and minimum (whiskers), and outliers that are more than the 1.5-fold interquartile range away from the quartiles (single dots). Primary tumor luminescence intensities of the 4 groups measured weekly from day 9 to 30 are shown. We found significant differences in the bioluminescence intensity between the 4 groups reflecting a significant difference in primary tumor viability (P = .006). The combination-treated tumors showed the lowest luminescence intensity of all groups with significantly lower luminescence intensity compared with the vehicle-treated tumors (P = .031) and highly significantly lower luminescence intensity compared with the 13cRA only-treated ones (P = .003). The 13cRA-treated tumors showed significantly and highly significantly higher luminescence intensity compared with the lovastatin- and vehicle-treated tumors (P = .048 and P = .006, respectively). B, Median tumor luminescence at 4 different time points from day 9 to 30 after tumor cell injection. The median tumor luminescence intensities of the 4 groups at 4 different time points are shown. There was a significantly slower increase of tumor activity over time in the combination-treated group compared with the vehicle-treated group (P = .023). Moreover, there was a highly significantly slower increase of tumor activity over time in the combination-treated group than in the 13cRA only-treated group (P = .003). The tumor activity of the lovastatin- and vehicle-treated mice also increased significantly slower over time than those of the 13cRA only-treated mice (P = .048 and P = .012, respectively). The lovastatin-treated group showed a (not statistically significantly) faster increase of tumor activity over time compared with the combination-treated group (P = .200) and a (not statistically significantly) slower increase of tumor activity over time compared with the vehicle-treated group (P = .232). C, Luminescence of lung and liver metastases at day 30. The 13cRA only-treated mice showed a significantly higher tumor activity in the liver than all the other groups (P ≤ .05). There was no obvious difference concerning liver metastases between all other groups. The combination-treated mice showed lowest tumor activity in the lung compared with all other groups. In the lovastatin- and the combination-treated group, there was a tendency of less tumor activity in the lung compared with the vehicle- and the 13cRA-treated group.