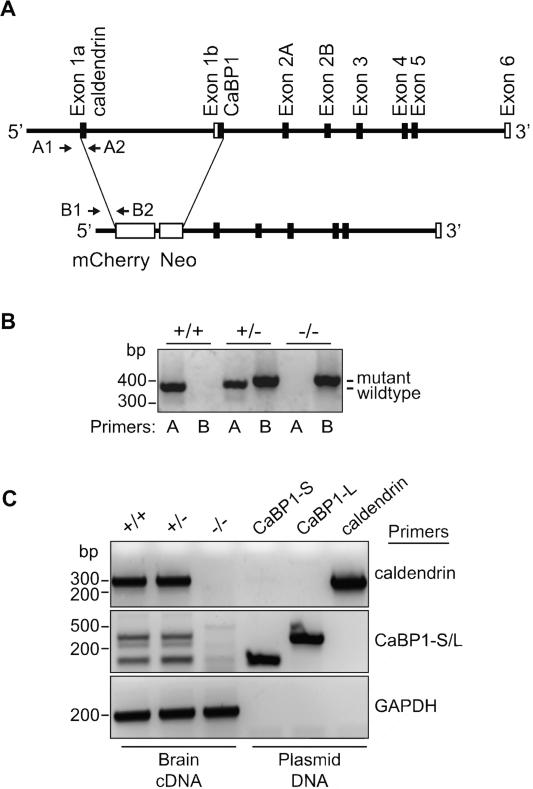
Figure 1. Disruption of the gene encoding CaBP1 and caldendrin.
(A) Schematic of the targeting construct that interrupts alternatively spliced exons 1a and exon 1b with the sequence encoding mcherry and neomycin resistance cassette (Neo). Locations of genotyping primers that identify wild-type (WT; A1,A2) and mutant (B1,B2) alleles are indicated. (B) PCR amplification with WT (A) and mutant (B) primers indicated in (A). Reactions were performed on genomic DNA isolated from WT (+/+), heterozygous (+/-), and homozygous (-/-) mice. (C) PCR amplification of caldendrin and CaBP1 variants (CaBP1-S/L) from the corresponding plasmid DNA or brain cDNA generated from +/+, +/-, or -/- mice. Amplification of GAPDH was performed as a positive control.