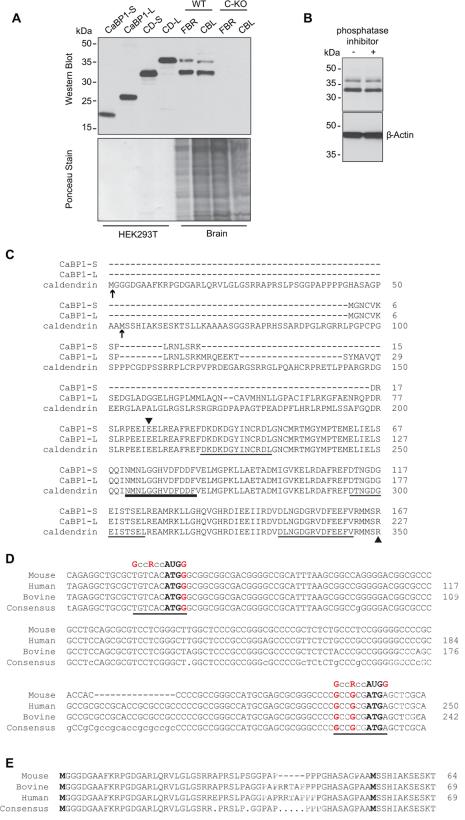
Figure 2. Detection of two variants of caldendrin but not CaBP1 in WT but not C-KO mouse brain.
(A) Western blot with CaBP1/CD antibodies (top panel) and ponceau staining of the same blot (lower panel) to indicate amount of protein loaded. Lanes 1-4 contain lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with cDNAs for CaBP1-S, CaBP1-L or caldendrin starting from Met53 (CD-S) or from Met1 (CD-L) according to the sequence numbering in (C). Lanes 5-8 contain lysates from the forebrain (FBR) or cerebellum (CBL) of WT or C-KO mice. (B) Effect of phosphatase inhibitor on bands detected by CaBP1/CD antibodies. Brain lysates were incubated with (+) or without (-) PhosStop phosphatase inhibitor prior to SDS-PAGE and western blotting with CaBP1/CD antibodies. Detection with β-actin antibodies was used to confirm equal loading in the lanes. (C) Alignment of the amino acid sequence of CaBP1 variants (CaBP1-S, CaBP1-L) and caldendrin. Potential alternative translation start sites for caldendrin are indicated by arrows. Arrowheads mark region corresponding to antigen used to raise CaBP1/CD antibodies. EF-hand domains are underlined, with bold line indicating non-functional EF-hand 2. Numbers correspond to amino acids of the corresponding mouse sequences. (D) Alignment of caldendrin N-terminal mRNA sequences from different species with canonical Kozak sequence (GccRccAUGG), indicated. Potential translation start sites are indicated in bold type. Highly conserved purine (R) at the -3 position and guanine residues at -6 and +4 are indicated in red. (E) Alignment of caldendrin N-terminal amino acid sequences from different species. In C-E, numbers in correspond to nucleotide or amino acid sequences available in GenBank. Alignments were generated using the MultAlin multiple sequence alignment application.