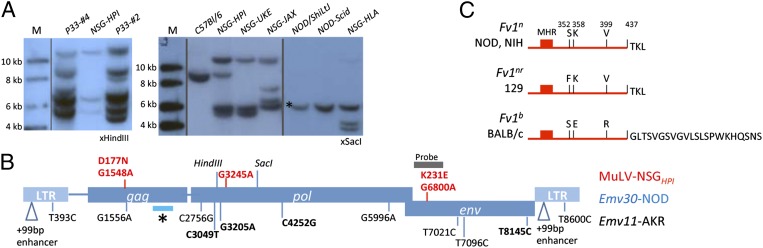
Fig. 3.
Analysis of somatic and germ-line MuLV integrations and host restriction mechanisms. (A) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from indicated mice. (B) Schematic representation of the Emv30 provirus and sequence variations between the infectious E-MuLV isolated from NSGHPI mice (in red) or the putative Emv11 provirus from AKR mice (in black). Nonsynonomous base changes are indicated in bold. Asterisk denotes the Fv1 interaction domain within the gag capsid protein. (C) Depiction of the carboxyl terminus of the Fv1 factor encoded by the indicated alleles. Sequence analysis of the Fv1 locus in NOD mice demonstrated 100% identity with the Fv1n allele of NIH 3T3 mice. The major homology region (MHR) and critical amino acids (single letter code) are indicated (20).