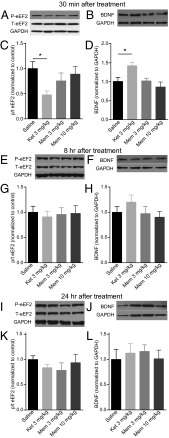
Fig. 4.
Differential effects of ketamine and memantine on eEF2 phosphorylation and BDNF protein expression at three different time points following treatment. (A and C) Densitometric analysis of phosphorylated eEF2 (P-eEF2) levels revealed ketamine caused a significant decrease in the ratio of P-eEF2/total eEF2 (T-eEF2) at 30 min, whereas memantine (3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg) did not have an impact on phosphorylation of eEF2. [ANOVA: F3,44= 3.579, *P = 0.021; Tukey’s post hoc analysis: saline vs. ketamine, *P = 0.018; saline vs. 3 mg/kg memantine, P = 0.569; saline vs. 10 mg/kg memantine, P = 0.930 (n = 10–13 per group)]. (B and D) Densitometric analysis of BDNF levels revealed that memantine did not have a significant effect on BDNF protein expression 30 min after injection; however, ketamine treatment caused a significant increase in BDNF protein [ANOVA: F3,49 = 5.893, P = 0.0016; Tukey’s post hoc analysis: saline vs. ketamine, *P = 0.02; saline vs. 3 mg/kg memantine, P = 0.999; saline vs. 10 mg/kg memantine, P = 0.745 (n = 12–15 per group)]. (E and G) Neither ketamine nor memantine caused a significant change in the levels of P-eEF2 8 h after injection, as shown by densitometric analysis (ANOVA: F3,21 = 0.0828, P = 0.969). (F and H) There was no change in the amount of BDNF protein in the hippocampus 8 h following injection with ketamine or memantine (ANOVA: F3,24 = 1.006, P = 0.407). (I and K) Densitometric analysis of P-eEF2 levels showed no difference in P-eEF2/T-eEF2 between saline and ketamine or memantine treatment 24 h after injection (ANOVA: F3,16 = 0.731, P = 0.552). (J and L) Densitometric analysis of BDNF protein showed no difference between saline, ketamine, or memantine treatment 24 h following injection (ANOVA: F3,25 = 0.206, P = 0.891). p/t, phospho/total.