Figure 4.
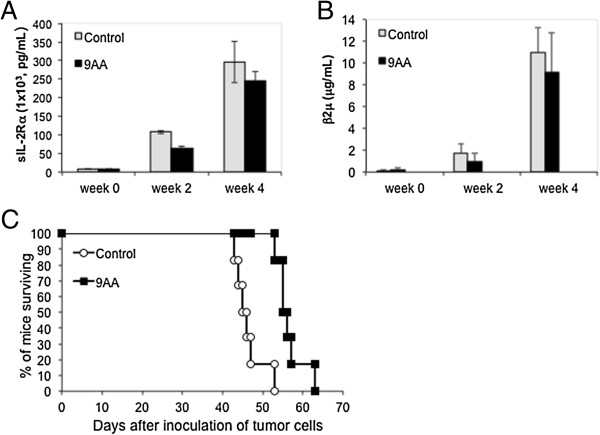
9AA modestly prolonged the survival period of MET-1 leukemia-bearing mice. (A) Serum levels of human soluble IL-2Rα (s IL-2Rα) during the course of treatment of NOD/SCID mice. At the beginning of the therapy, the serum levels of sIL-2Rα for the control group and 9AA group were 6,749 pg/mL and 7,223 pg/mL, respectively. Two weeks after therapy, the serum values of the control group and 9AA treated group were 107,606 pg/mL and 64,538 pg/mL, respectively (p = .11). Four weeks after therapy, the values of sIL-2Rα between the control group and the 9AA group were 295,636 pg/mL and 245,642 pg/mL, respectively (p = .17). (B) The mean serum β2μ levels during the course of treatment in NOD/SCID mice. At the beginning of the therapy, the serum levels of β2μ for the control group and 9AA group were 0.07 μg/mL and 0.17 μg/mL, respectively. Two weeks after therapy, the serum values of the control group and 9AA treated group were 1.76 μg/mL and 0.99 μg/mL, respectively (p = .11). Four weeks after therapy, the values of β2μ were 11 μg/mL and 9.2 μg/mL for the control group and the 9AA group, respectively (p = .32). (C) Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrating 9AA prolonged the survival of mice bearing the MET-1 leukemia. The control group mice died between days 43 and 53, and its median survival duration was 45.5 days. The 9AA group mice died between days 53 and 63, and its median survival duration was 55.5 days. Compared to the control group, there was a significant prolongation of the survival of the mice treated with 9AA (p = .0056).
