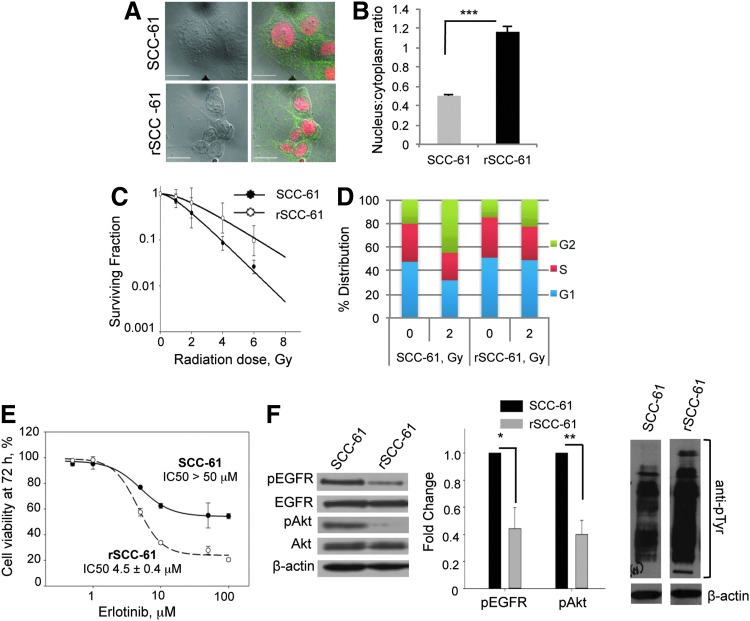
FIG. 1.
rSCC-61 exhibits increased resistance to radiation and increased sensitivity to Erlotinib in comparison to SCC-61. (A) Cell morphology. The SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells were immunostained with anti-EGFR antibodies, and the nucleus was stained with Topro-3-iodide to mark the cell and nuclear boundaries, respectively. Images were acquired using the Zeiss LSM510 confocal microscope. The scale bars represent a distance of 20 μm. (B) Quantification of nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio (NCR). The NCR was quantitated using ImageJ software from confocal images shown in panel A (***p<0.001, n=50 cells). (C) Clonogenic assay to determine the response to radiation. The survival curves of SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells are shown in response to increasing doses of radiation. Data were fit to multi-target and linear-quadratic models. The values of D0, α and β parameters are listed in Supplementary Table S1. (D) Cell-cycle analysis. The percent distribution of SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells in the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle was determined at 24 h after treatment with the 0 and 2 Gy radiation doses. (E) Cell viability in response to Erlotinib treatment. MTT assay was used to measure cell viability at 72 h post-treatment with Erlotinib (0, 0.5, 1.0, 10.0, 25.0, 50.0, and 100.0 μM). The percentage of viable cells was calculated relative to the untreated control. (F) Western blot analysis of EGFR and Akt phosphorylation. SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against pEGFR, total EGFR, pAkt, total Akt, total pTyr, and β-actin and quantified using ImageJ (pEGFR: *p=0.022, n=3; pAkt: **p=0.004, n=3). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.