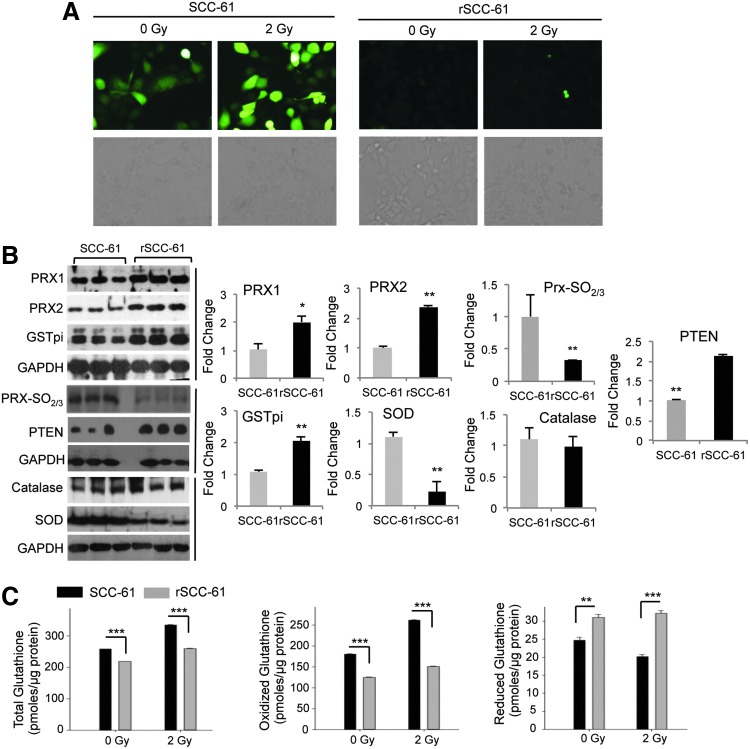
FIG. 6.
rSCC-61 have decreased ROS and reduced DNA damage. (A) ROS imaging analysis. DCF fluorescence images of ROS in SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells before and after treatment with radiation (control −0 Gy and 2 Gy). Images were captured using the Arcturus PixCell II laser capture microscope under 20×objective. (B) Western blot analysis of proteins involved in the antioxidant system in rSCC-61 and SCC-61. Three out of five biological replicates are shown here for Prx1 and 2, Prx-SO2/3, PTEN, GSTpi, SOD, and catalase. Quantification is based on all five replicates (n=5) and taking into account the differences in GAPDH (Prx1: *p=0.03; Prx2: **p=0.003; Prx-SO2/3: **p=0.0012; GSTpi: **p=0.0014; SOD: **p=0.004; Catalase: p>0.05; PTEN: **p=0.009). (C) Quantification of glutathione. Glutathione (total, oxidized and reduced) in SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells was measured at 1 h after treatment with 2 Gy of ionizing radiation. Quantification is based on three biological replicates, and the respective p-values are ***p<0.001 for total and oxidized glutathione (0 Gy and 2 Gy) and reduced glutathione (2 Gy); **p=0.005 for reduced glutathione (0 Gy). DCF, dichlorofluorescein; GSTpi, glutathione S-transferase pi; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars