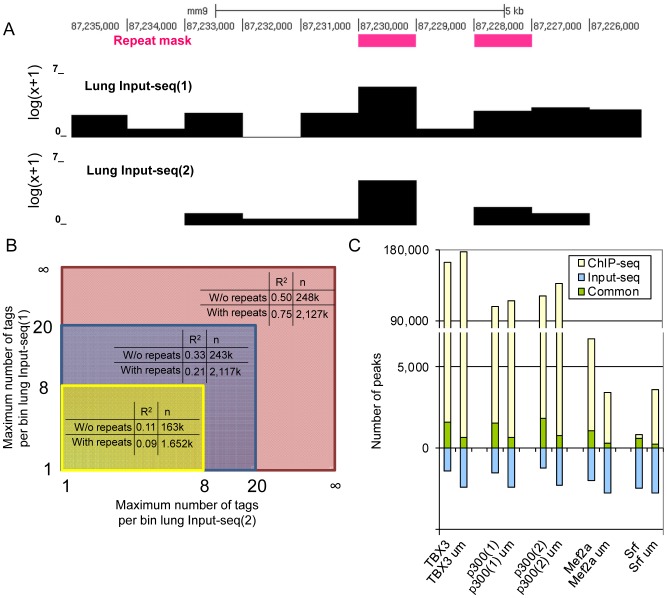
Figure 1. Correlation between Input-seq datasets depends on repeated sequences.
A. UCSC genome browser snapshot showing tag counts (log scale) in 1 KB bins of two replicate Input-seq datasets. High tag counts are related to annotated genomic repeats. B. Correlation between tag counts in two replicate Input-seq datasets for bins without or with genomic repeats (yellow area: bins with tag counts between 1 and 8, blue: between 1 and 20, red: between 1 and infinity). Bins without any tags were excluded from the analysis because they might be the result of unmappable regions. C. The small overlap (green) between peaks called in ChIP-seq datasets (yellow) and an Input-seq dataset (blue) is significantly reduced when only uniquely mappable (um) reads are considered in peak calling. This is effect is independent of the number of called peaks.