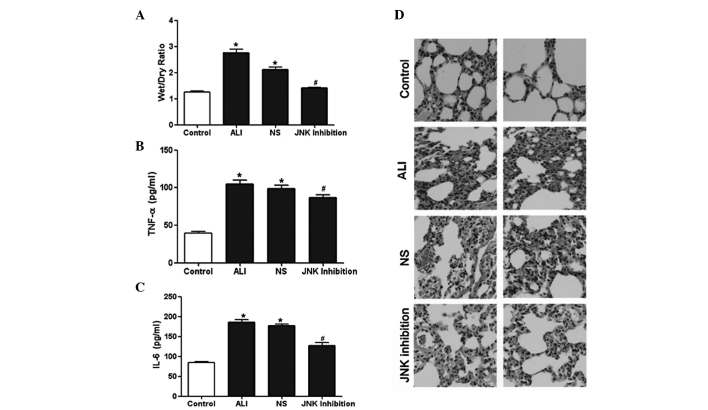
Figure 1.
SP600125 attenuates LPS-induced ALI in rats in vivo. (A) Following LPS injection with or without SP600125 treatment, the rats were sacrificed and their left lower lungs were obtained in order to determine the wet/dry weight ratio. *P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 vs. ALI. (B and C) An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was performed to determine the expression of TNF-α and IL-6 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the rats from each group. *P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 vs. ALI. (D) Lung tissue sections were stained using hematoxylin and eosin to determine the pathological alterations with or without SP600125 treatment. Representative images are shown from each group (magnification, ×200). Column 1 and 2 show different views in the same group. ALI, acute lung injury; NS, normal saline; JNK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.