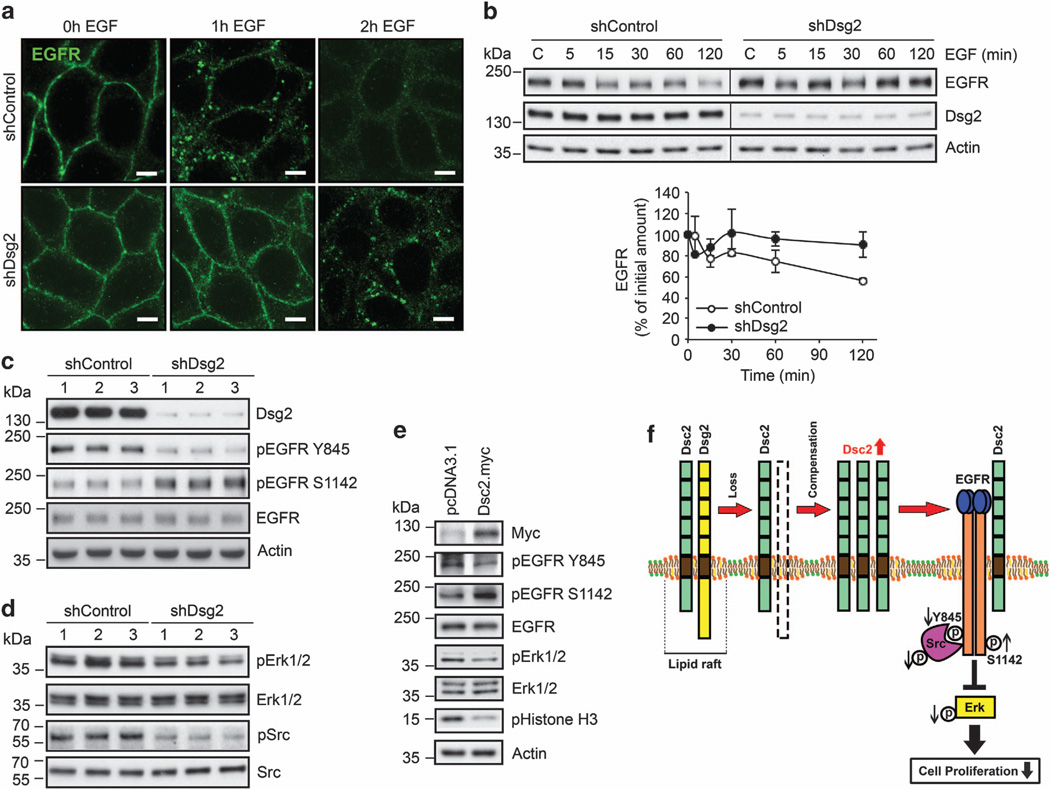
Figure 2.
Loss of Dsg2 suppresses EGFR signaling. (a) Immunofluorescence labeling confocal microscopy demonstrating EGF-induced EGFR internalization. shControl and shDsg2 SK-CO15 cells were treated with 20 ng/ml EGF (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) at different time course. Green, EGFR (Cell Signaling); scale bar is 5 µm. (b) Immunoblot analysis of EGFR and Dsg2 in shControl and shDsg2 SK-CO15 cells at steady state and after the addition of EGF. The cells were incubated with 20 ng/ml EGF 5–120 min. The graph displays the relative EGFR expression normalized to actin as determined by densitometric analysis. Mean ± s.e.m. The data were averaged from three independent experiments. (c) Immunoblot analysis against pEGFR Y845, pEGFR S1142 and EGFR levels in shControl and shDsg2 SK-CO15 cells. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis against Dsg2 (AH12.2), pEGFR Y845 (Cell Signaling), pEGFR S1142 (ECM Biosciences, Versailles, KY, USA) and EGFR. (d) Immunoblot analysis of EGFR signaling cascade in shControl and shDsg2 SK-CO15 cells. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis against Dsg2 (AH12.2), pErk1/2 T202/Y204 (Cell Signaling), Erk1/2 (Cell Signaling), pSrc Y416 clone 9A6 (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and Src clone M259 (ECM Biosciences). (e) Immunoblot analysis demonstrating EGFR signaling cascade and pHistone H3 in Dsc2 overexpressing SK-CO15 cells. Cells were transfected with 2.5 µg of pcDNA3.1 empty vector (control) or 2.5 µg of the pcDNA3.1-Dsc2-myc expression vector using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) in Opti-MEM medium (Invitrogen). The cells were collected 48 h post transfection. Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis against Myc Tag clone 9B11 (Cell Signaling), pEGFR Y845, pEGFR S1142, EGFR, pErk1/2, Erk1/2 and pHistone H3. (f) A model for how Dsg2 regulates cell proliferation. Loss of Dsg2 inhibits intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and tumor growth through inactivation of the EGFR, Erk and Src signaling pathway. Knockdown of Dsg2 results in increased Dsc2 protein that compensates for Dsg2 loss, which leads to a decrease active (Y845) EGFR and increase in inactive (S1142) EGFR resulting in less cell proliferation. Our model is further supported by a decrease in Src and downstream Erk activation, which are involved in regulated cell proliferation through further effectors. Downregulation of Dsg2 negatively regulates cell proliferation and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Actin in b, c and e was used as a loading control.