Figure 13.1.
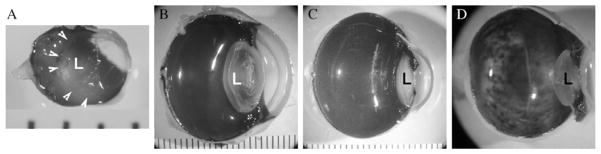
The space occupied by the lens relative to the vitreous cavity differs across species and dictates the surgical approach. In the mouse (A), the lens (L) occupies the majority of the cavity and so injections are usually carried out with a trans-choroidal approach. In larger animals ((B) dog, (C) monkey) and (D) humans, the lens is much smaller relative to the rest of the eye and so injections can be carried out from an anterior approach under direction visualization. Arrowheads in (A) indicate the borders of the lens. Distance between each bar in (A)–(C) is 1mm.
