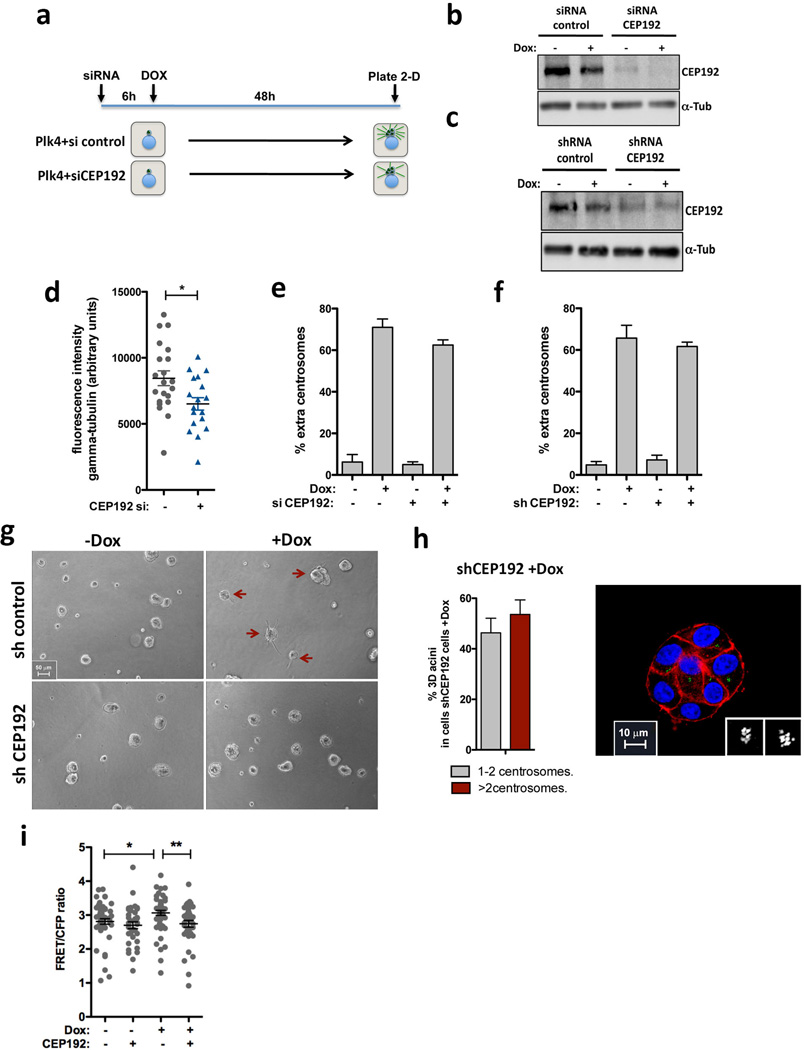
Extended Data Figure 10. Depletion of Cep192 suppresses the invasive properties of cells with centrosome amplification.
a, Scheme of the experimental design to induce centrosome amplification in cells depleted of Cep192 by siRNA. Transient overexpression of Plk4 is induced 6hrs after siRNA to allow efficient centrosome overduplication. As expected, after depletion of Cep192 for 48hrs, cells are partially compromised in their ability to overduplicate centrosomes after Plk4 OE44. b, Western blot showing efficient depletion of Cep192 after 48hrs treatment of cells with Cep192 siRNA. c, Western blot showing partial depletion of Cep192 by shRNA. d, Quantification of centrosomal γ-tubulin after depletion of CEP192 by siRNA for 48hrs. Similar results were observed with Cep192 esiRNA (not shown). Of note, at least for a three-day period, cells remain viable after Cep192 knockdown. nctr.siRNA=22; nCEP.siRNA=20. Error bars represent mean ± SE. Quantification of centrosome amplification after depletion of Cep192 by siRNA (e) or shRNA (f). Error bars represent mean ± SE from 3 independent experiments. g, Bright field images of acini after 4 days in 3-D culture, demonstrating that partial Cep192 depletion by shRNA does not significantly impair cell growth or the formation of acini. Red arrows indicate the invasive acini. h, Right: Quantification of Plk4-mediated centrosome amplification in cells depleted of Cep192 after 4 days in 3-D cultures showing that these cells still carry extra centrosomes. Error bars represent mean ± SE from 3 independent experiments. Left: Normal acini displaying centrosome amplification after partial knockdown of CEP192. Cells were stained for F-actin (red), centrioles (centrin1-GFP, green) and DNA (blue). Scale bar: 10µm. i, Levels of active Rac1 measured by FRET after CEP192 depletion. nctr.siRNA−Doc=51; nctr.siRNA+Doc=35 nCEP.siRNA−Dox=53; nCEP.siRNA+Dox=37. Error bars represent mean ± SE. All the p-values were derived from unpaired two-tailed t-test (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.005).