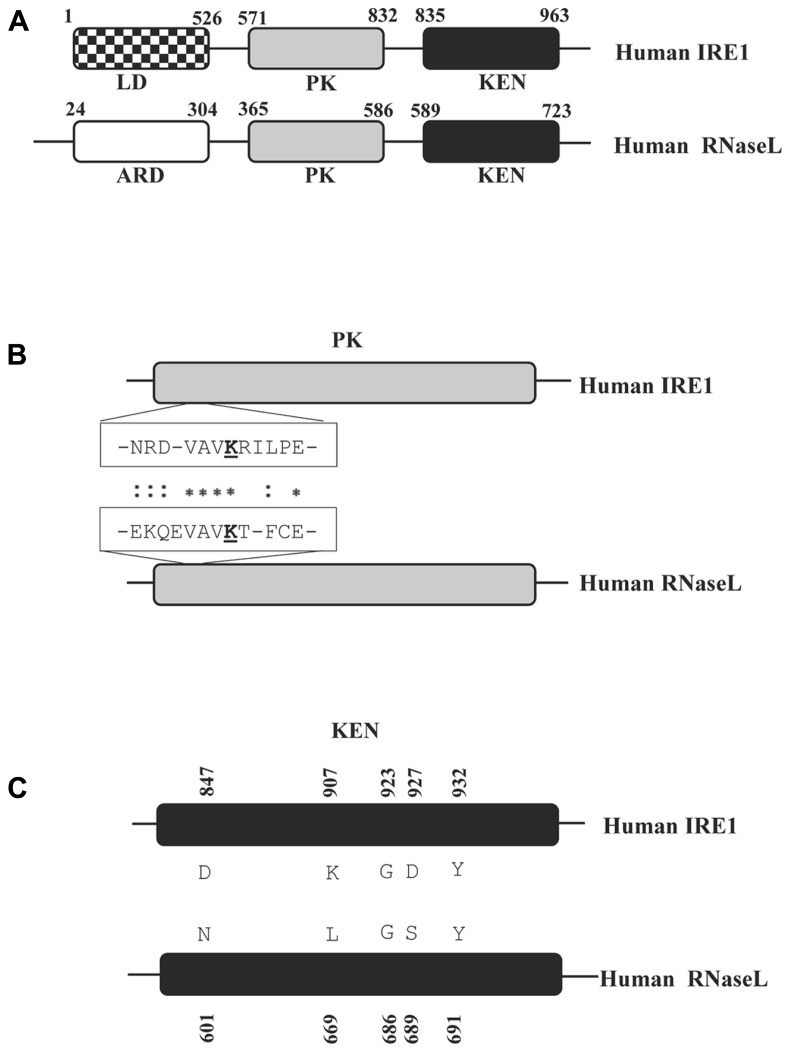
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of distinct protein domains in human RNaseL and IRE1. (A) The domains homologous between RNaseL and IRE1 are shaded identically. The domain name abbreviations denote the following: ARD = ankyrin repeat domain; LD = luminal domain; PK = protein kinase domain; KEN = kinase extension nuclease domain. The amino acid positions bordering each domain are numbered. The schematic drawings are not according to scale. (B) ClustalW alignment of primary sequence from a segment of the PK domain indicating amino acid residues which are important for interacting with nucleotide cofactors. The conserved lysine residues, critical for this interaction (K599 for IRE1 and K392 in RNaseL) are underlined. (C) Alignment of the KEN domains in RNaseL and IRE1. The amino acids highlighted and numbered in IRE1 are critical for the IRE1 RNase activity (Tirasophon et al., 2000).