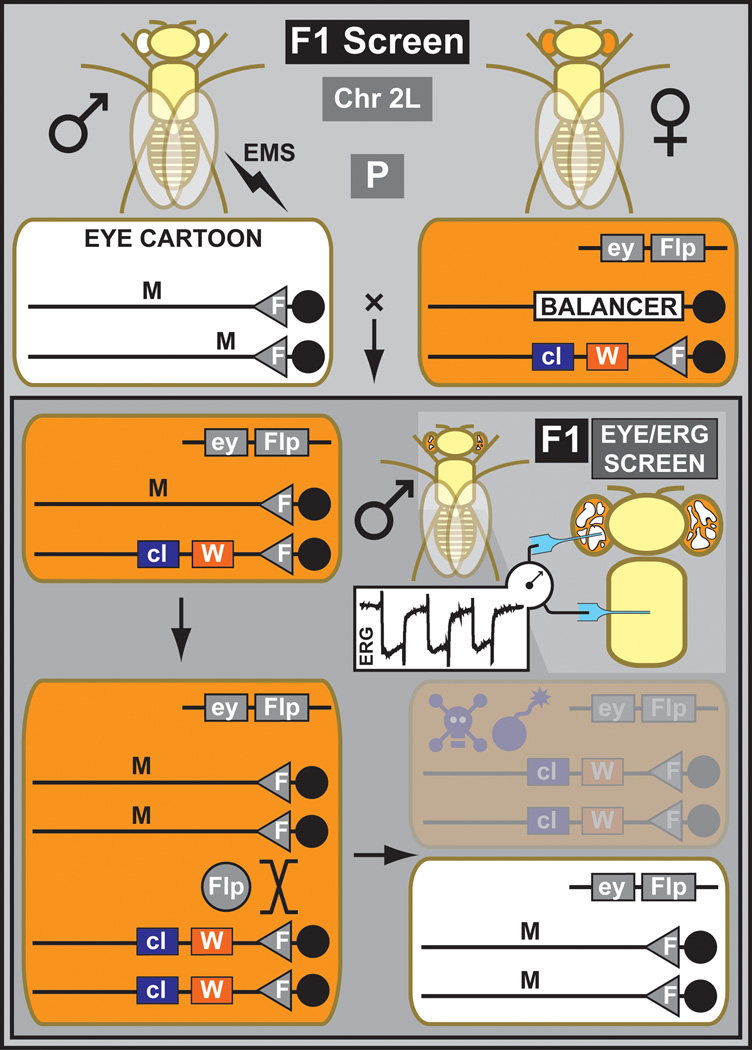
Figure 1. Outline of a mitotic F1 screen for chromosome 2L.
Mutagenized males containing a chromosome 2 with an FRT site on arm 2L are crossed to females containing the same FRT carrying chromosome but with an additional dominant eye color marker, white+ (W), and recessive cell lethal (cl). In addition, the females carry a transgene that drives the FLP protein under the control of eyeless promoter (ey). This cross is the parental (P) generation. In the next generation (F1), the FLP generates mitotic clones exclusively in the eye. Due to the presence of a recessive cell lethal, homozygous WT clones die, and many ommatidia become homozygous mutant, facilitating phenotypic analyses based on morphology or an electrophysiological assay like the elecroretinogram (ERG). Flies are recovered, and propagated for stock keeping and further analysis.