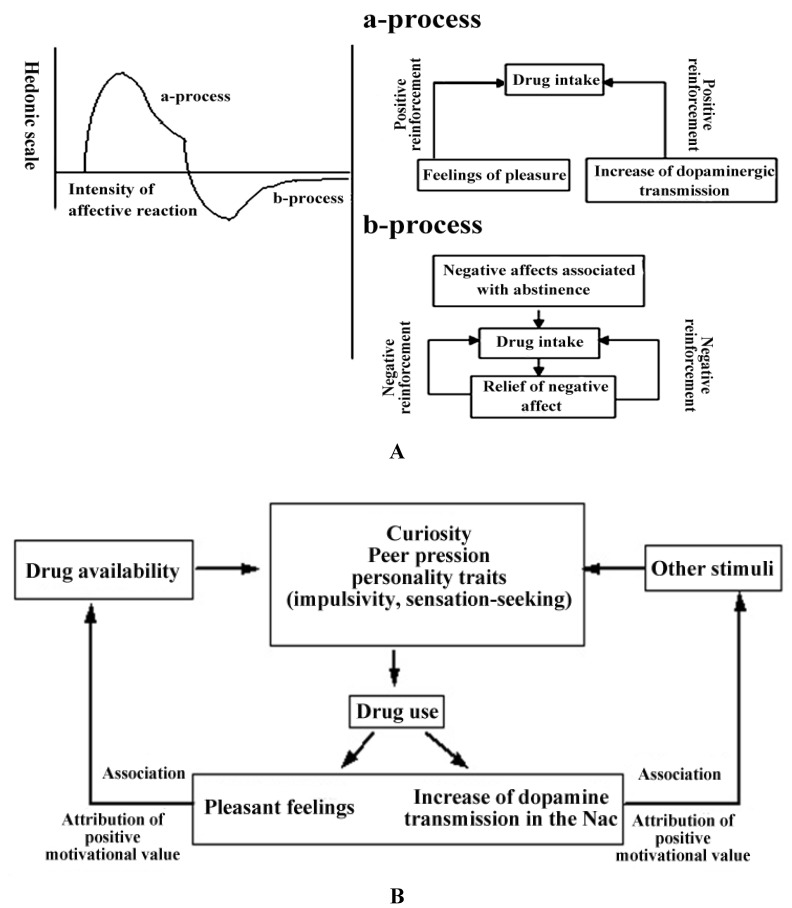
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic illustration of the model of the hedonic dysfunction postulated by Koob & Le Moal [12]. Adapted with permission from Martin-Soelch [28]. Copyright 2002 Peter Lang. a-Process corresponds to the positive hedonic effects of the substance of abuse; b-process corresponds to the counterregulatory homeostatic reaction of the brain that elicits negative affective states. (B) Illustration of the learning processes involved in the acquisition of dependence and in the attribution of incentive motivation to drug related cues. Adapted with permission from Martin-Soelch [28]. Copyright 2002 Peter Lang.