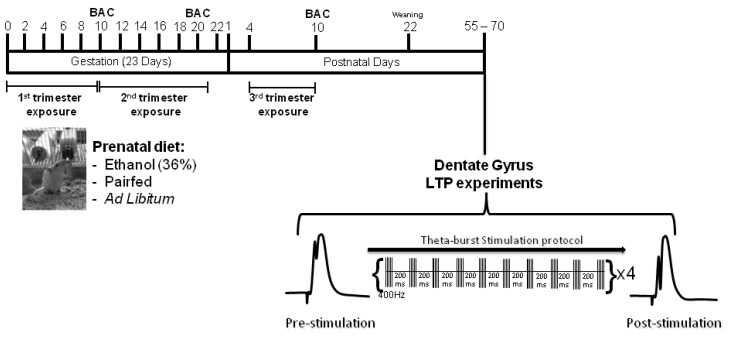
Figure 3.
Experimental Timeline. On GD1 pregnant dams were assigned to one of seven treatment groups: Ad libitum controls, 1st trimester equivalent ethanol exposure, 1st trimester equivalent pair-fed, 2nd trimester equivalent ethanol exposure, 2nd trimester equivalent pair-fed, 3rd trimester equivalent ethanol exposure, or 3rd trimester equivalent pair-fed (see text for a detailed explanation of the various groups). Blood samples to assess BAC were taken on GD 10 for the 1st trimester equivalent exposure condition, GD20 for the 2nd trimester equivalent exposure condition, and PND 10 for the 3rd trimester equivalent exposure condition. When animals reached experimental age (PNDs 55–70) they were used for in vivo electrophysiological experiments to examine LTP in the DG of the hippocampus. Basal recordings were first obtained by administering a pulse (0.12 ms in duration) at 0.067 Hz (pre-stimulation). Once a stable baseline was observed for at least 15 min, LTP was induced by applying TBS consisting of 10 bursts of 5 pulses at 400 Hz with an inter-burst interval of 200 ms, which was repeated 4 times at 30 s intervals. The pulse duration was changed to 0.25 ms during TBS. Following TBS, baseline stimulation resumed for 60 min (post-stimulation).
Abbreviations: Blood alcohol concentration (BAC); Dentate gyrus (DG); Gestational day (GD); Long-term potentiation (LTP); Postnatal day (PND); Theta burst stimulation (TBS).