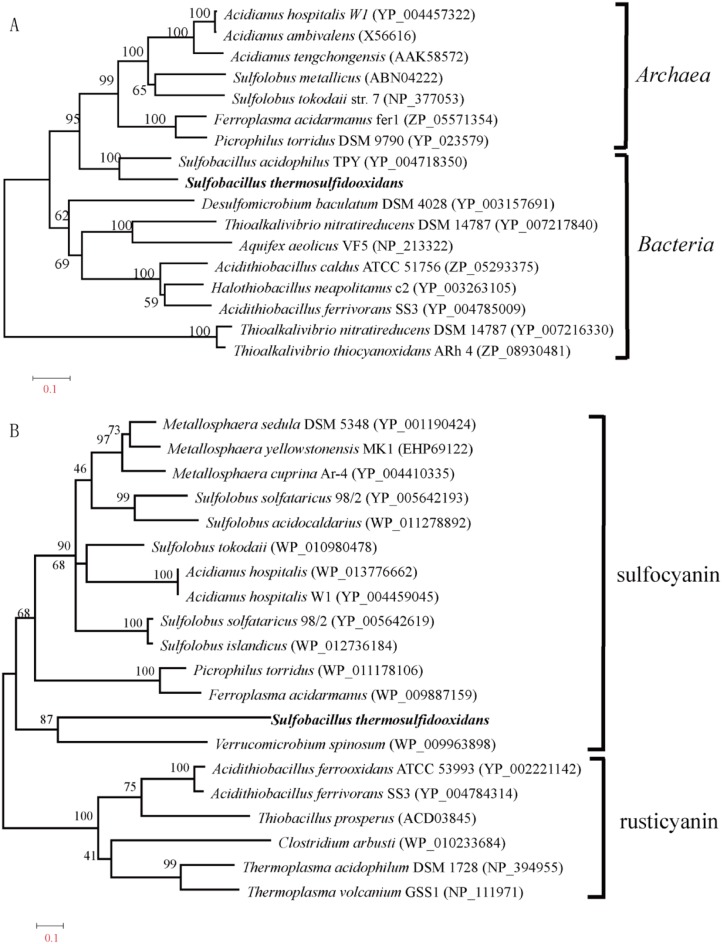
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of key genes related with the oxidation of inorganic sulfur compounds and ferrous iron.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of sulfur oxidase reductase based on an alignment of 334 amino acid positions with the neighbor-joining method. The numbers associated with the branches refer to bootstrap values (confidence limits) resulting from 1,000 replicate resamplings. The scale represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. S. thermosulfidooxidans are shown in bold. (B) Phylogenetic tree of sulfocyanin/rusticyanin proteins of archaea and bacteria based on an alignment of 263 amino acid positions with the neighborjoining method. The numbers associated with the branches refer to bootstrap values (confidence limits) resulting from 1,000 replicate resamplings. The scale represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. S. thermosulfidooxidans are shown in bold.