Figure 2.
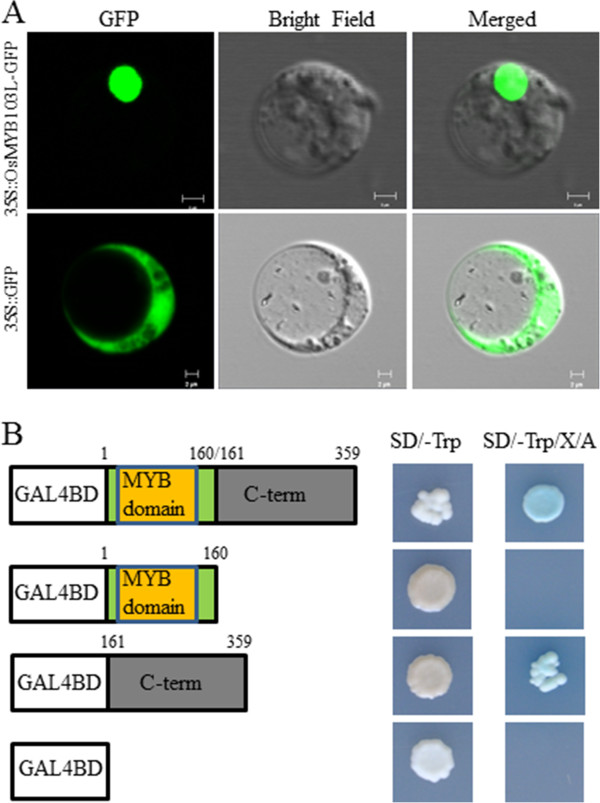
Subcellular localization and transactivation analysis of OsMYB103L. (A) Subcellular localization of OsMYB103L. GFP and OsMYB103L-GFP fusion gene under the control of the CaMV35S promoter were expressed transiently in rice protoplasts. Left to right: GFP fluorescence image, transmission image and merged image. Bar = 2 μm. (B) Transactivation analysis of different regions of OsMYB103L fused with the GAL4 DNA binding domain in yeast. The full-length, N-terminal MYB DNA-binding domain (1–160 amino acids) or the C-terminal putative activation domain (161–359 amino acids) were respectively cloned into pBD-GAL4 vector containing AUR1-C and MEL1 reporter genes and then transformed into yeast host strain Y2HGold. The pBD vector was used as a negative control. The expression of AUR1-C confers strong resistance to the highly toxic drug Aureobasidin A (Aba). The activities of α-galactosidase encoded by MEL-1 were examined by X-α-gal staining.
