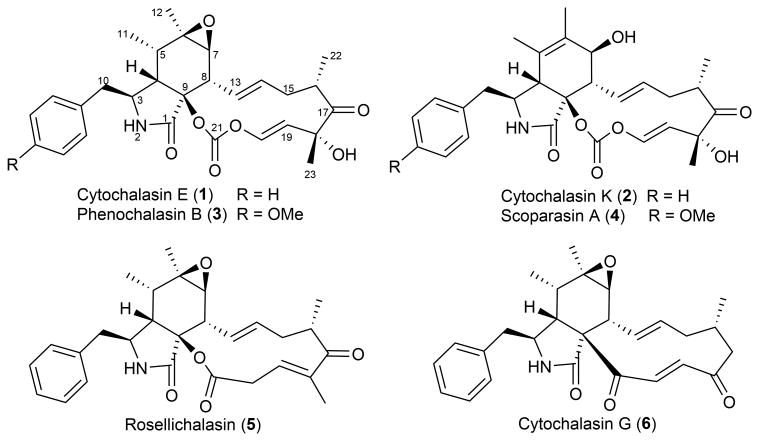
Figure 1.
Cytochalasins with different oxidation outcomes in the macrocyclic portion. Compounds 1-4 contain a vinyl carbonate group of interest at C21 within the thirteen-membered macrocycle that is fused to an isoindolone bicyclic scaffold. Other members of the large cytochalasin family are less oxidized at the corresponding carbonate carbon than 1-4, including esters such as rosellichalasin (5) and ketones as in cytochalasin G (6).