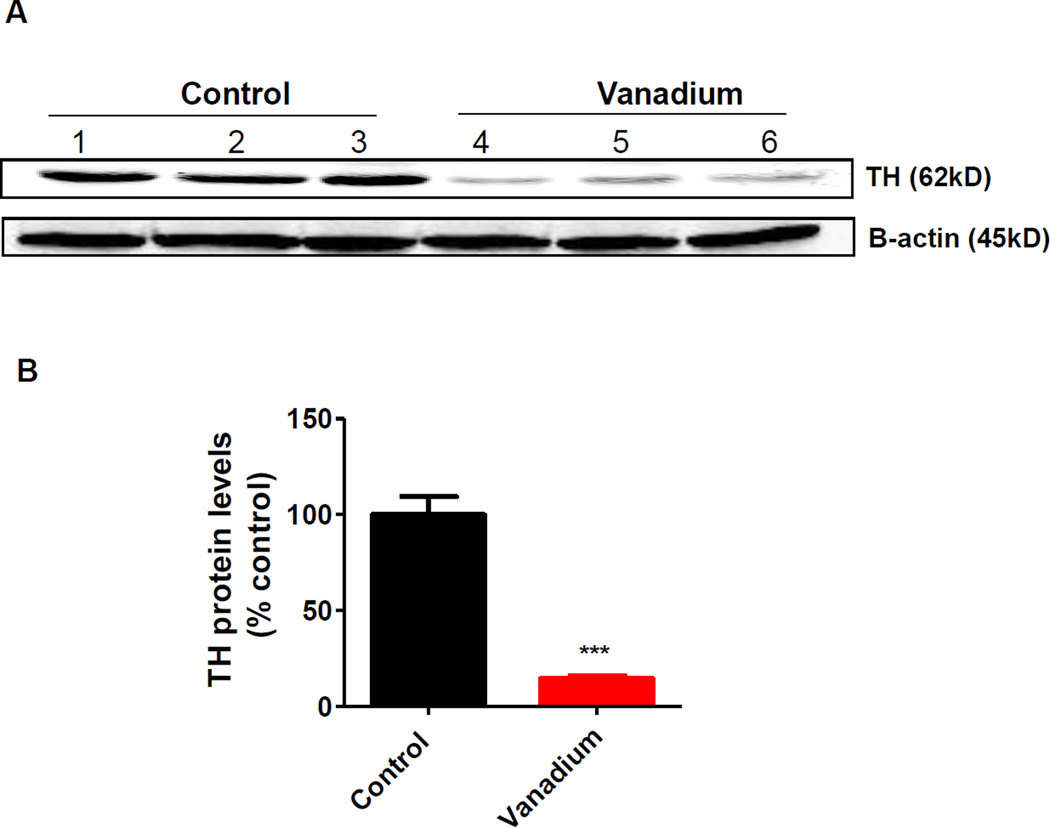
Fig. 4. Effect of intranasally administered vanadium on TH expression levels in olfactory lobes.
Male C57 black mice (n ≥ 3 per group) were intranasally administered 182 µg of V2O5 in 50 µL of deionized water three times a week for one month. The vehicle control animals were administered deionized water. At the end of the treatment animals were sacrificed and TH expression was detected in the olfactory lobe by Western blot using mouse monoclonal antibody against TH. (A) A representative Western blot analysis of TH expression in control and vanadium treated mice. β-actin immunoblot was used to confirm equal protein loading in each lane. (B) The bands were quantified for densitometric analysis and data are expressed as a percentage of vehicle-treated bands. Asterisks (***, p < 0.001) indicate a significant difference between treatment and control group means ± S.E.M.