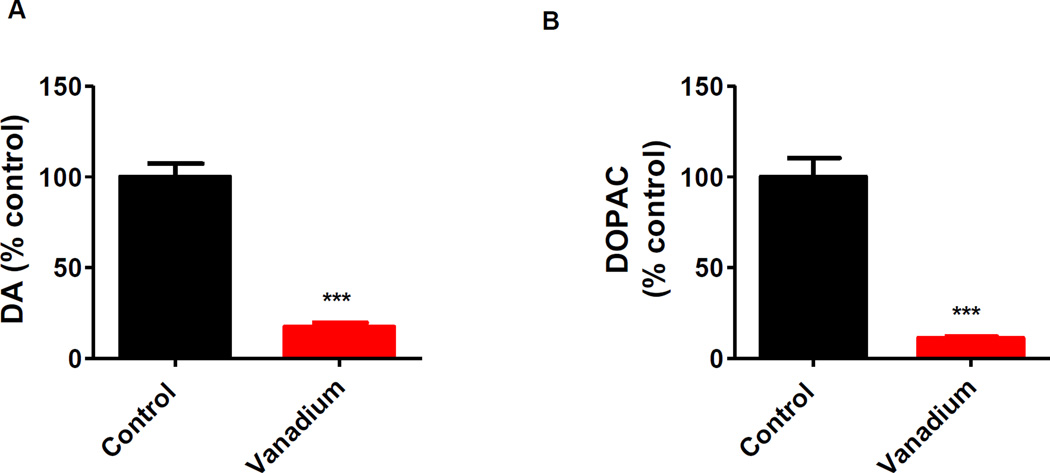
Fig. 6. Effects of intranasally administered vanadium on olfactory bulb dopamine and DOPAC levels.
Male C57 black mice (n ≥ 5 per group) were intranasally administered 182 µg of V2O5 in 50 µL of deionized water three times a week for one month. The vehicle control animals were administered deionized water. Animals were sacrificed following the last treatment, and the neurochemical analysis (A, dopamine; B, DOPAC) was performed in olfactory lobe tissues using HPLC. Asterisks (***, p < 0.001) indicate a significant difference between treatment and control group means ± S.E.M.