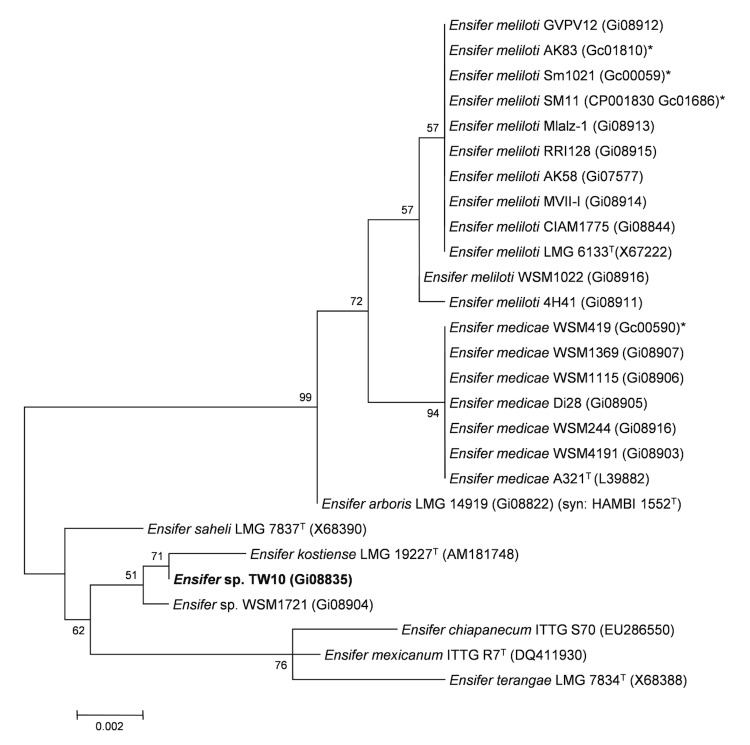
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of Ensifer sp. TW10 (shown in bold print) to other Ensifer spp. in the order Rhizobiales based on aligned sequences of the 16S rRNA gene (1,290 bp internal region). All sites were informative and there were no gap-containing sites. Phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA, version 5 [19]. The tree was built using the Maximum-Likelihood method with the General Time Reversible model [20]. Bootstrap analysis [21] with 500 replicates was performed to assess the support of the clusters. Type strains are indicated with a superscript T. Brackets after the strain name contain a DNA database accession number and/or a GOLD ID (beginning with the prefix G) for a sequencing project registered in GOLD [22]. Published genomes are indicated with an asterisk.