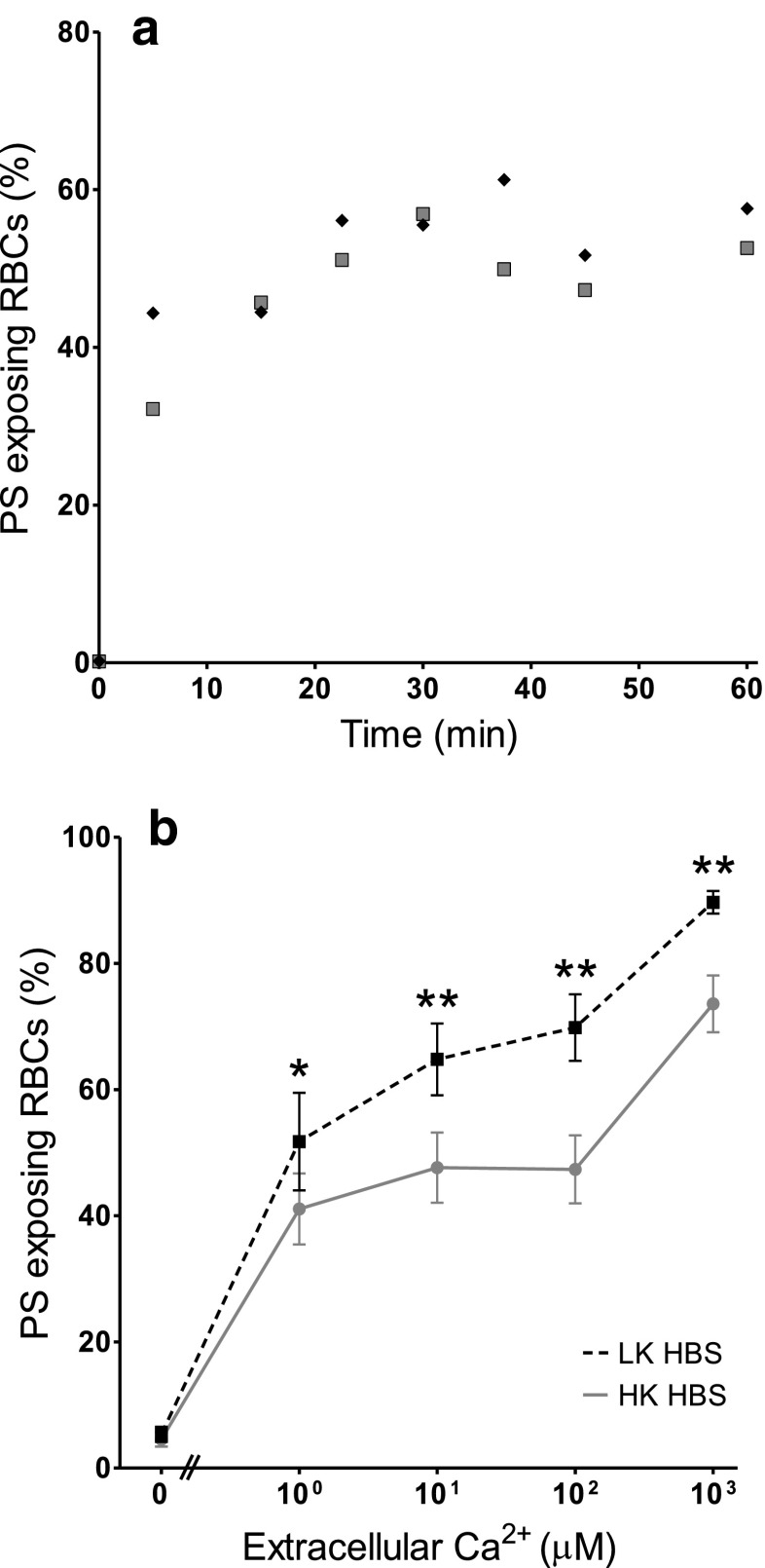
Fig. 1.
Ca2+-induced exposure of phosphatidylserine (PS) in red blood cells (RBCs) from patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). a Time course: RBCs were treated with the ionophore bromo-A23187 (2.5–6 μM) for up to 60 min in high potassium-containing (HK) saline with 100 μM extracellular [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]o). Symbols represent duplicate measurements from a single sample. b Ca2+ dependence: RBCs (0.5 % haematocrit, Hct; final [DMSO] <1 %) were treated with ionophore (2.5–6 μM) for 30 min, in HK or low potassium-containing (LK) saline, with [Ca2+]o varied between 0 μM and 1 mM. Symbols represent means ± SEM, n = 12. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.002 between PS exposure in RBCs incubated in HK or LK saline