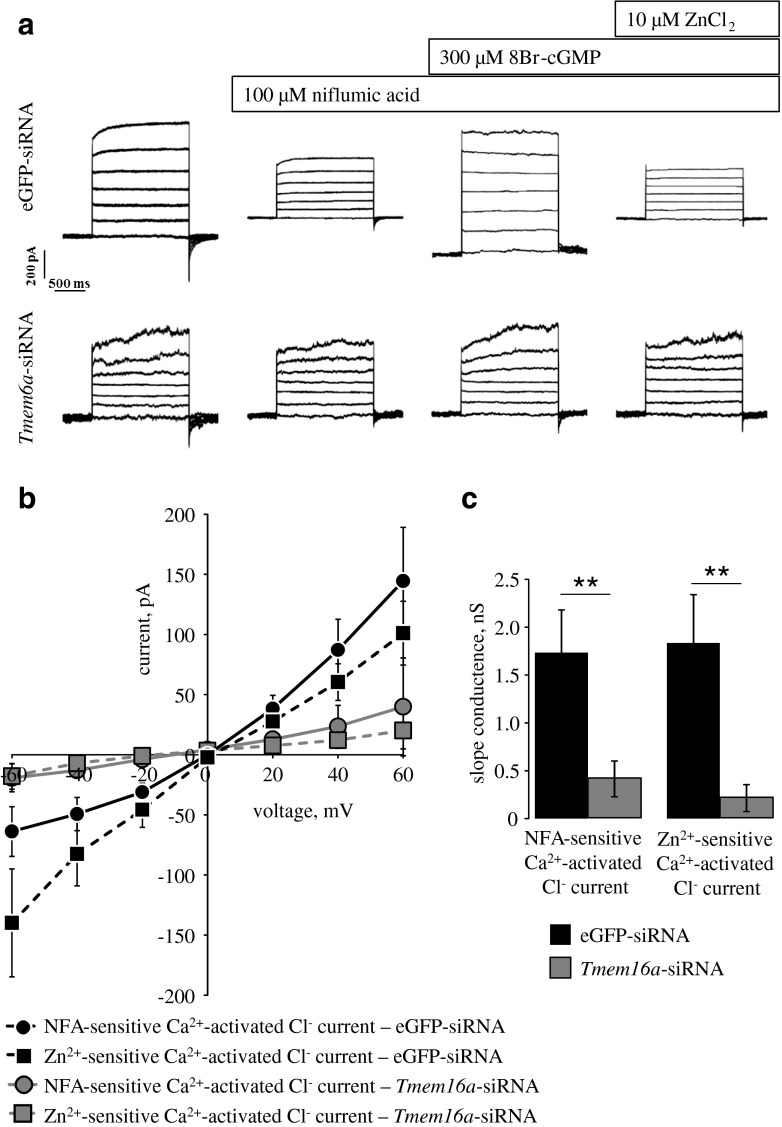
Fig. 3.
TMEM16A downregulation suppresses both the niflumic acid-sensitive and the Zn2+-sensitive Ca2+-activated Cl− currents in SMCs isolated from rat mesenteric small arteries transfected with Tmem16a-siRNA in vivo. a Representative recordings from SMCs transfected with siRNA directed against eGFP (eGFP-siRNA) or with Tmem16a-siRNA. Membrane currents were recorded by stepping holding voltage between −60 and +60 mV with 20 mV increments. Membrane currents were consequently recorded under control conditions, after incubation with 100 μM niflumic acid, 300 μM 8Br-cGMP, and 10 μM ZnCl2, as indicated. b Averaged current–voltage characteristics for the niflumic acid (NFA)-sensitive and the Zn2+-sensitive Ca2+-activated Cl− currents calculated from the experiments similar to those shown in a. c The whole-cell slope conductances (between −20 and +20 mV) of two currents in b measured in SMCs transfected with either siRNA directed against eGFP (eGFP-siRNA) or with Tmem16a-siRNA. n = 9–13; **P < 0.01