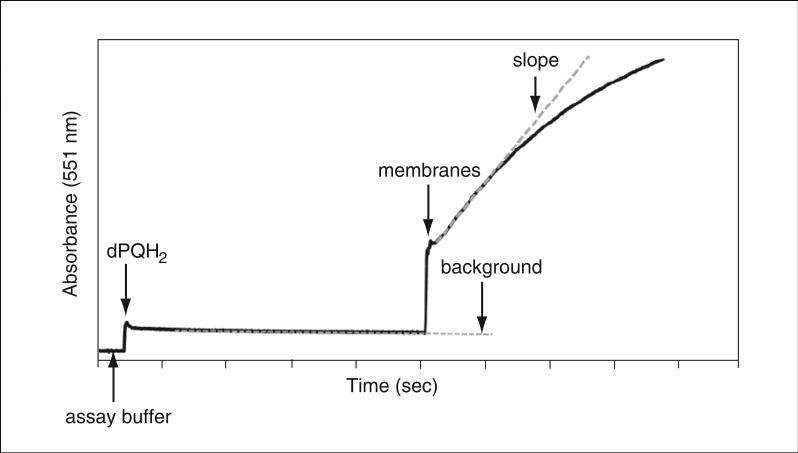
Figure 29.7.6.
Assay of Cyt b6f electron transfer activity. The Cyt b6f complex in cyanobacterial thylakoid membranes catalyzes electron transfer from the electron donor decylplastoquinol (dPQH2) to the electron acceptor cytochrome c (Cyt c). dPQH2 is added to the assay buffer and a baseline is recorded. The electron transfer reaction is initiated by addition of cyanobacterial membranes. Reduced Cyt c has an absorbance peak at 551 nm. As one electron is required to reduce one molecule of Cyt c, estimation of Cyt c reduction per unit time yields the catalytic activity of the Cyt b6f complex (calculations performed from initial electron transfer rate; slope shown as gray dotted line). Since Cyt b6f concentration cannot be determined in intact membranes, the specific rate is expressed in units of electrons transferred per 103 chlorophyll per second. The slow background rate of electron transfer from dPQH2 to Cyt c in the absence of Cyt b6f (gray dotted line marked background) is subtracted from the slope of b6f-catalyzed electron transfer.