Figure 1.
BRCA2 Interacts with Plk1 through Residues Mutated in Breast Cancer
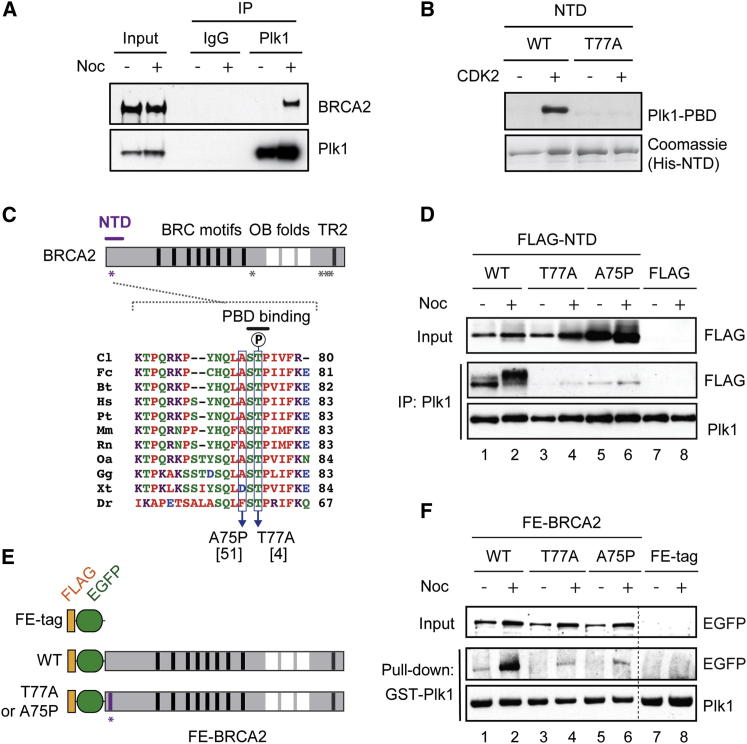
(A) WCEs from untreated or nocodazole (Noc)-treated HeLa cells were used for IP with anti-Plk1 or control rabbit IgG, and coprecipitated BRCA2 was detected with BRCA2 antibody.
(B) Recombinant His-NTD was phosphorylated by recombinant CDK2/cyclin A in vitro and the interactions between Plk1-PBD and BRCA2 fragments were detected by far-western blotting.
(C) BRCA2 domain architecture, highlighting BRC motifs (black bars), oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding (OB) folds (white blocks), and the TR2 motif (gray bar). Locations of minimal PBD-binding sequences (asterisks) and the N-terminal BRCA2 fragment, NTD (purple bar) are shown. Bottom panel shows multiple amino acid sequence alignment surrounding the PBD-binding motif within the NTD. Breast cancer-associated mutations at residues A75 and T77, and the putative Plk1-binding region are also indicated. The reported numbers of breast cancer patients (Breast Cancer Information Core) are shown in brackets. Cl, dog; Fc, cat; Bt, cattle; Hs, human; Pt, chimpanzee; Mm, mouse; Rn, rat; Oa, platypus; Gg, chicken; Xt, frog; Dr, fish.
(D) FLAG-tag or FLAG-BRCA2 NTD variants (WT, T77A, and A75P) were transiently expressed in HEK293T cells, and following treatment with nocodazole, interaction with endogenous Plk1 was analyzed by IP with Plk1 antibody.
(E) Schematic diagram of FLAG-EGFP (FE)-tagged full-length BRCA2 variants, representing FLAG (orange) and EGFP (green). An amino acid substitution within the NTD (asterisk) that impairs Plk1 interaction is also indicated.
(F) FE-BRCA2 WT, T77A, A75P variants, or FE-tag were conditionally expressed in HEK293 Flp-In T-REx cells and treated with nocodazole, where indicated. The association of the BRCA2 variants with an exogenously expressed GST fusion of Plk1 was detected following GST pull-down.
See also Figure S1.