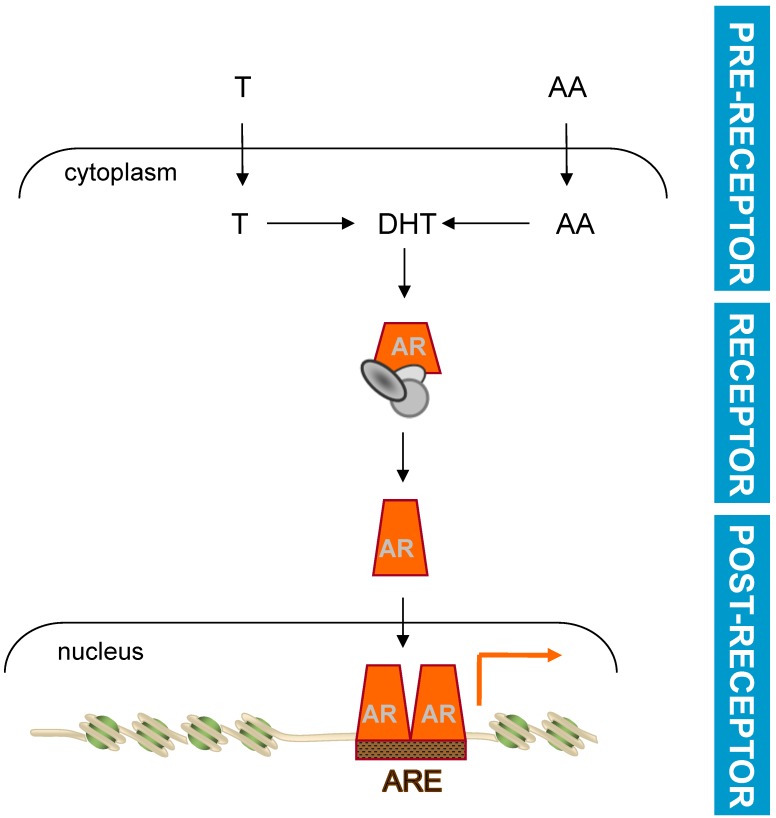
Figure 1.
Basic mechanism of androgen action. Testosterone (T) or adrenal androgens (AA) are converted to DHT in CaP cells. Ligand activation induces a conformational change and nuclear translocation of AR. Within the nucleus, AR binds AREs in target genes to regulate their transcription and modulate CaP cell behavior. Pre-receptor level ADT interferes with AR ligand production. Receptor level ADT impedes AR-ligand interaction. Post-receptor level ADT exploits AR-dependent action downstream of AR for therapeutic intervention.