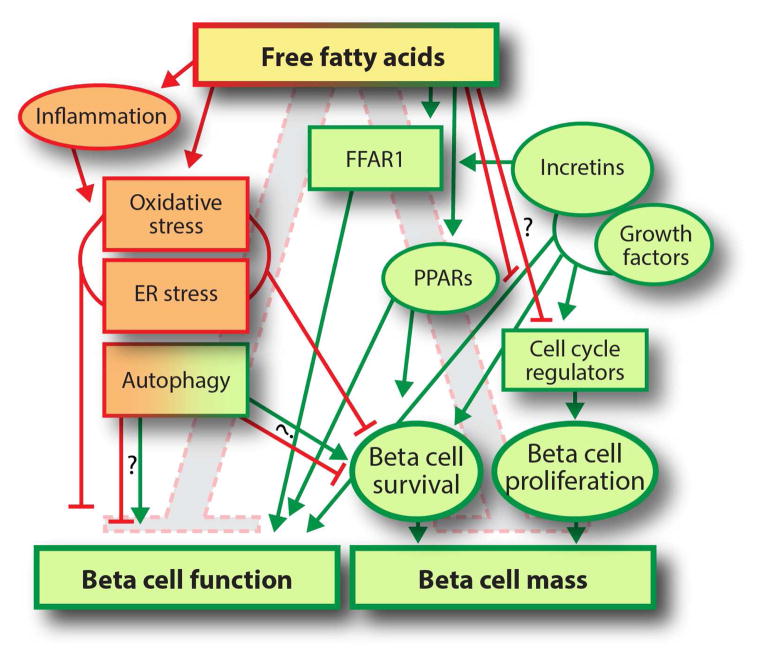
Figure 1.
Free fatty acids exert both positive (green) and negative (red) effects on beta cell mass and function. FFAs signal through receptors such as FFAR1 and PPARs, or through metabolic pathways as comprehensively reviewed in [1, 2]. Positive effects are mediated predominantly through FFAR1 and PPARs. Negative effects are mediated through inflammation, cellular stress mechanisms, and possibly inhibition of the cell cycle. Negative effects of FFAs are modulated by growth factors and incretins. Whether autophagy plays a net positive or net negative role is controversial.