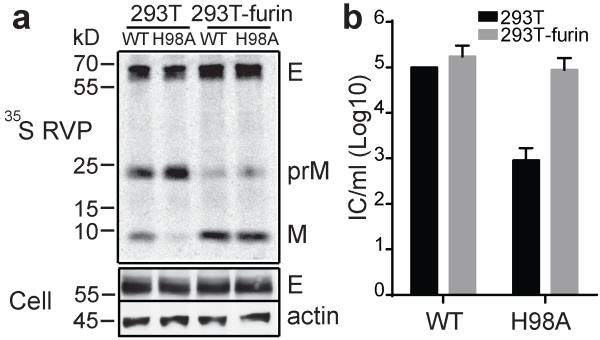
Figure 4. prM H98A inhibits DENV RVP maturation and infection.
a. prM H98A inhibits prM processing. RVPs were produced in control or furin-overexpressing 293T cells by co-transfection of plasmids encoding the WT or mutant DENV1 WP structural proteins and a WNV replicon plasmid encoding the non-structural proteins plus a GFP reporter. Starting at 12h post-transfection, cells were radiolabeled at 29 °C for 36 h. RVPs and cell lysate samples were harvested and analyzed as in Fig. 3a. Data are a representative example of three independent experiments. Quantitation of western blots and 35S-labeling showed that E protein expression in mutant-infected cells was 1.2-1.3-fold that of the WT, and efficiency of RVP secretion was 0.8-0.9-fold that of WT (n=2). Full scans of the phorphorimages and blots are in Supplementary Fig. 4. b. prM H98A inhibits DENV RVP infectivity and is rescued by furin over-expression. WT and mutant RVPs were produced in control or furin-overexpressing 293T cells as in 4A but without radiolabeling. The resultant RVPs were titered on Vero cells. Data are the mean and standard deviation (SD) of four independent experiments, with WT titers produced in 293T cells normalized to 105 infectious units/ml.