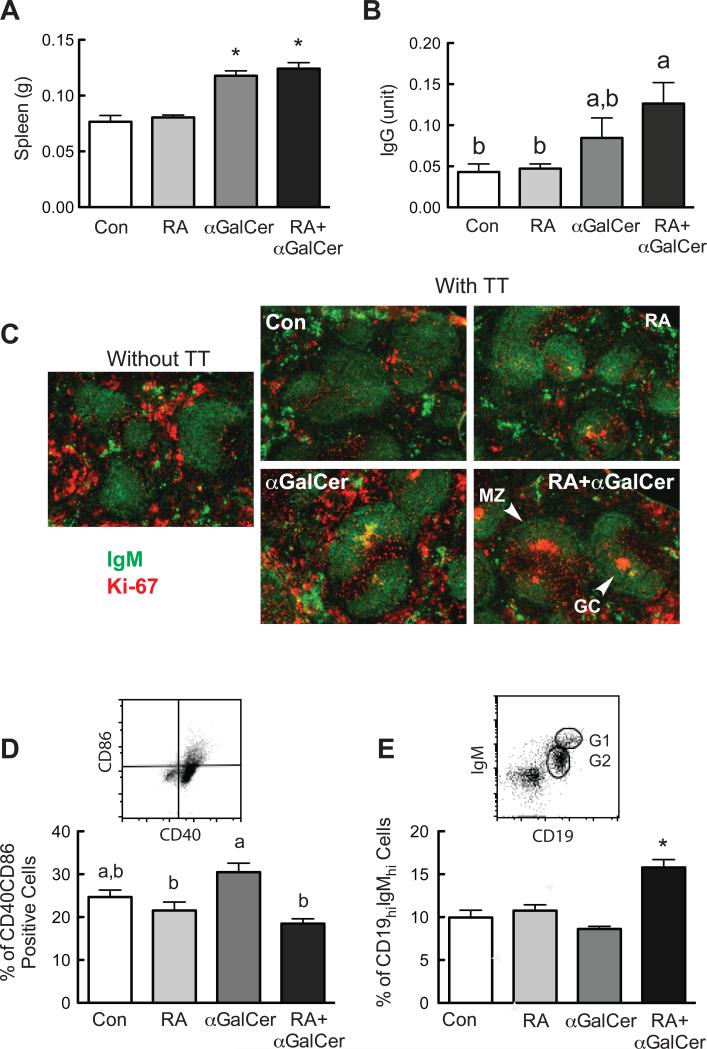
Fig. 4.
RA and αGalCer regulate B cell differentiation in vivo. Spleens from the immunized animals with and without RA and/or αGalCer treatment (refer to Material and Methods) were collected and subjected flow cytometry analysis and immunofluorescent staining. A. Spleen weight is increased after αGalCer treatment. B. Serum TT-specific IgG levels determined by ELISA. C. Immunofluorescent staining of mouse spleens showing the spleen follicle with marginal zone (MZ) and germinal center (GC) identified by IgM (Green) and Ki-67 (Red). D. Comparison of CD40-CD86 positive cells after treatments. Splenocytes were first gated on CD19+ cells, and then analyzed for their CD40-CD86 staining. E. RA and αGalCer increased CD19hi-IgMhi positive B cells. The in vivo experiment was performed more than three times with n=3 to 5 each time.