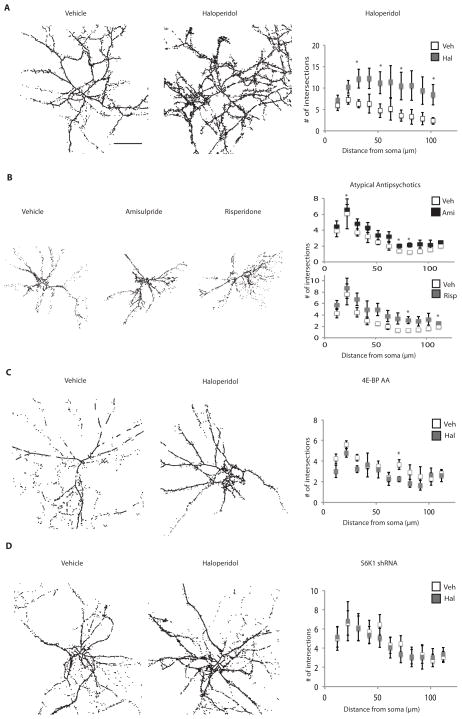
Figure 4. Haloperidol treatment leads to increased morphological complexity in striatal DARPP32-positive neurons.
Primary striatal neurons were cocultured with wild-type cortical neurons (2:3 ratio), grown to DIV14, and exposed for 24 hours to either vehicle, haloperidol, amisulpride, or risperidone. Neurons were stained with an antibody against DARPP32 and morphological complexity was quantified by Sholl analysis. Images shown are line enhanced for visualization. The number of intersections within 100 μm of the soma was quantified on images without line enhancement. (A) The effect of haloperidol on morphological complexity of wild-type striatal neurons. (n=4, p<0.000001, cells analyzed = 19 for vehicle treated, 20 for haloperidol treated) (B) The effect of the indicated atypical antipsychotics on morphological complexity of wild-type striatal neurons. Risperidone (n=3, p=0<0.002, cells analyzed = 24 for vehicle treated, 23 for drug treated); amisulpride (n =3, p<0.01, cells analyzed = 24 for vehicle treated, 21 for drug treated). (C) The effect of haloperidol on striatal neurons expressing 4E-BP AA. 4E-BP AA-expressing striatal neurons were cocultured with wild-type cortical neurons as described above, then induced with doxycycline overnight and exposed to haloperidol for 24 hours. Scholl analysis was performed on cells that were stained positive for both DARPP32 and the HA tag on the 4E-BP AA. (n=3, p = 0.05 decrease, cells analyzed = 12 for vehicle treated, 13 for haloperidol treated). (D) The effect of haloperidol on striatal neurons in which S6K1 is knocked down. S6K1 shRNA-expressing striatal neurons were cocultured with wild-type cortical neurons as described above and exposed to haloperidol for 24 hours. Scholl analysis was performed on cells that were stained positive for both DARPP32 and GFP that marks the shRNA-expressing cells. (n=3, p=not significant). Scale bar indicates 50 μm. All graphs shown are average ± SEM. p ≤ 0.06 is indicated by the asterisk.