Table 1. Assignments of the Sites for the Two Primary Tyr• Intermediates in Cytochrome c Peroxidase (CcP) and the Reaction with the Guaiacol Substrate, Based on the EPR Characterization of the Designed CcP Variants Shown in Panels A and B of Figures 1 and 4.
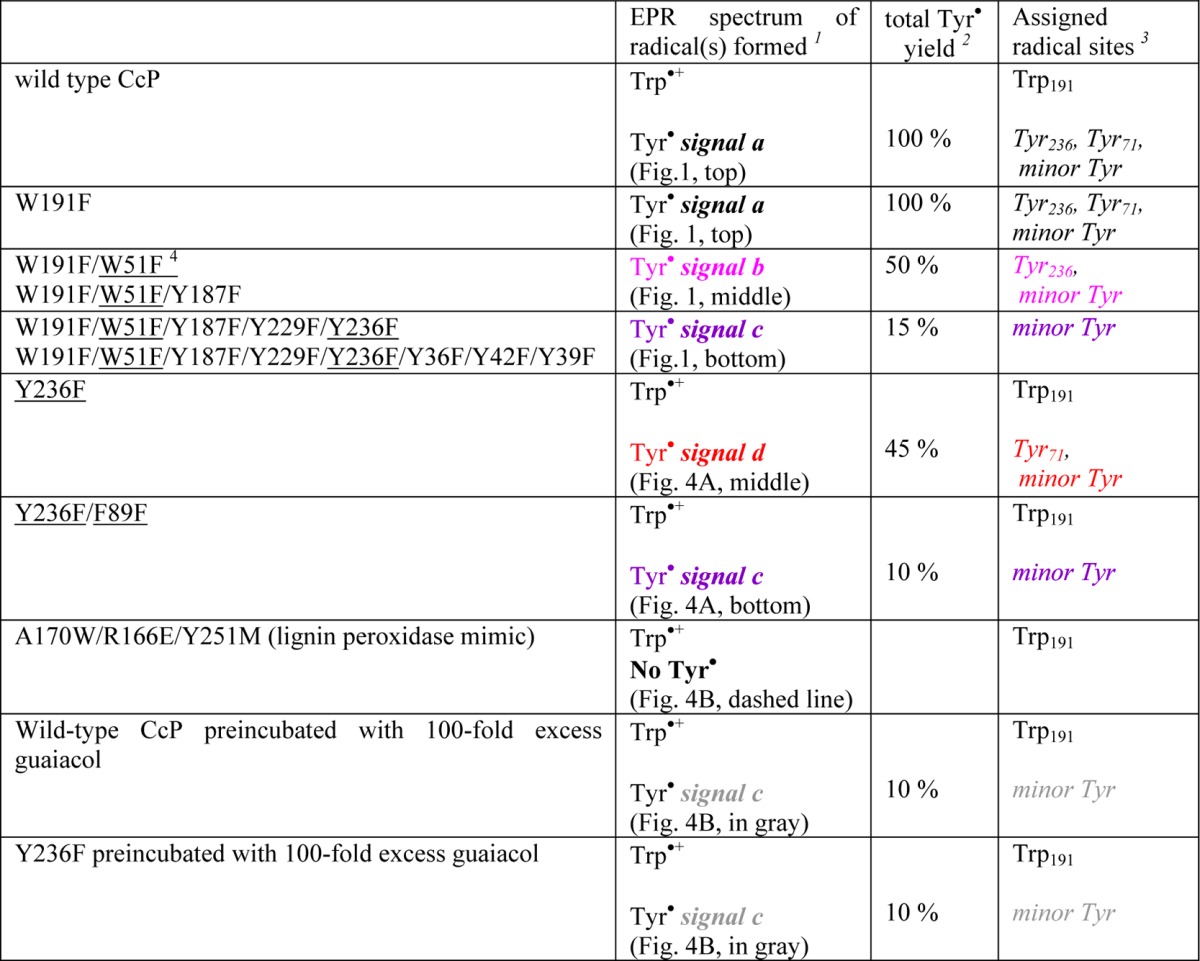
The colors highlight the four different Tyr radical signals that correspond to those in Figures 1 and 4.
The percentage of Tyr radical(s) yield for the variants was estimated by comparison of the signal intensity with that of the wild-type CcP with H2O2 (considered the 100% yield).
Tyr sites that contribute to the Tyr• EPR signal in each sample.
The underlined residues are those inducing EPR spectral changes, consistent with suppression of the primary Tyr radical sites. The W51F variant indirectly impeded the formation of Tyr71• by the disruption of the long-range electron transfer pathway, while the F89L variant destabilized radical formation on Tyr71 by inducing steric effects on its microenvironment (see the text).
