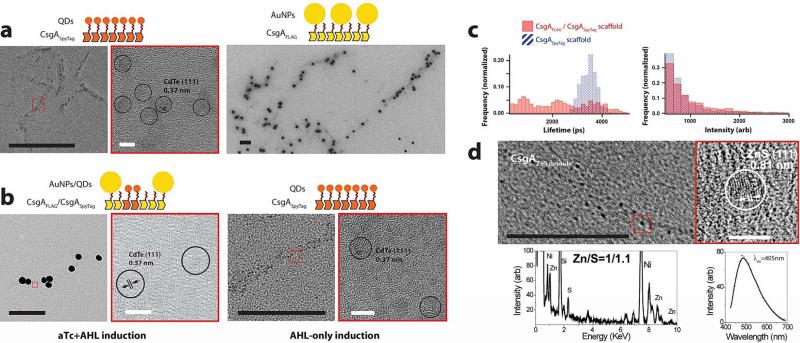
Figure 6. Assembly and tuning of functional AuNP-QD heterostructures and nucleation of fluorescent ZnS QDs on cell-synthesized curli fibrils.
a, CsgASpyTag fibrils specifically bind CdTe/CdS QDs conjugated to the SpyCatcher protein; the CdTe cores of QDs are seen under HRTEM. CsgAFLAG fibrils are specifically bound by anti-FLAG antibodies which are in turn bound by 40nm AuNPs conjugated to secondary antibodies. CsgA fibrils do not bind either CdTe/CdS QDs conjugated to SpyCatcher or 40nm AuNPs conjugated to antibodies (Supplementary Fig. 23a, b). b, A mixed population of aTcReceiver/CsgAFLAG and AHLReceiver/CsgASpyTag cells produced curli templates for either AuNP-QD heterostructures (cofibrils of CsgAFLAG and CsgASpyTag) or QD-only assemblies (CsgASpyTag fibrils) depending on whether they were induced by both aTc and AHL, or AHL only, respectively. c, Cell-patterned curli fibrils enable the tuning of stimuli-responsive inorganic-organic materials. AuNP-QD assemblies patterned on CsgAFLAG/CsgASpyTag scaffolds (solid red bars) exhibited different fluorescence lifetime and intensity properties than QD-only assemblies patterned on CsgASpyTag scaffolds (hashed blue bars). d, CsgAZnS peptide fibrils nucleated ~5nm nanoparticles with a cubic zinc blende ZnS (111) structure and approximately 1:1 ratio of zinc and sulphur. The particles were fluorescent, with an emission peak at 490nm when excited at 405nm. Control CsgA fibrils nucleated few such particles (Supplementary Fig. 23c). In a), b), and d) black scale bars are 200nm and white scale bars are 5nm; the images outlined by red boxes are zoomed-in versions of the inset red boxes.